如果自己搞不定可以找诗檀软件专业ORACLE数据库修复团队成员帮您恢复!
诗檀软件专业数据库修复团队
服务热线 : 13764045638 QQ号:47079569 邮箱:service@parnassusdata.com
ORA-8103是我们Database Consultant 经常要遇到的一个问题,了解ORA-8103的成因非常重要。
【数据恢复】利用构造ROWID实现无备份情况下绕过ORA-1578、ORA-8103、ORA-1410等逻辑/物理坏块问题
简单来说ORA-8103 的主要成因有2类:
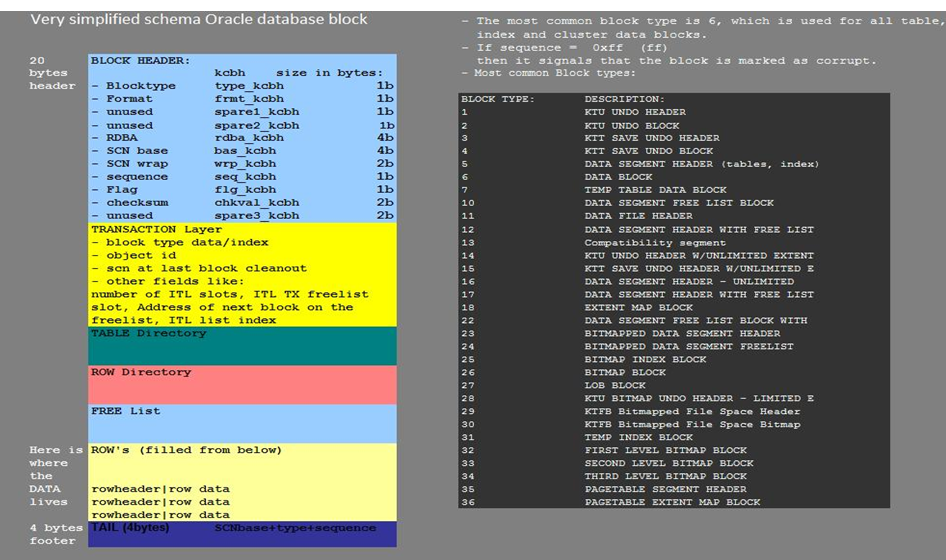
- 数据块的 block type 类型 是 无效的 或者读出来的块类型与Oracle期望的不一致。 例如 Oracle 认为该数据块的类型为data(type=6),但实际却不是。
- 数据块中的data_object_id 和 数据字典中的data_object_id不匹配
针对ORA-8103问题 我们优先推荐一些措施:
ORA-08103问题的诊断最好是能生成8103错误的ERROR STACK TRACE, 在TRACE中会记录具体引发8103的对象的OBJ和OBJD,这便于我们定位可能存在corruption的对象。
问题在于往往前台进程遇到ORA-08103错误不会在后台生成TRACE文件,这需要我们手动设置8103 触发ERRORSTACK的EVENTS:
ALTER SYSTEM SET EVENTS ‘8103 TRACE NAME ERRORSTACK LEVEL 3’;
解决思路包括:
1. 通过OBJD和DBA定位到具体的表名和块号
2. 有条件的情况下对该表做一个analyze .. validate structure
3. 有条件的情况下对该表所在tablespace做一个 dbms_space_admin.ASSM_TABLESPACE_VERIFY
4. 有条件的情况下move这张表或者相关的分区,尝试绕过该问题
5. 有条件的情况下降该表或分区移动到MSSM表空间上,绕过该问题
execute dbms_space_admin.tablespace_verify(‘&tablespace_name’)
oradebug setmypid
oradebug tracefile_name
execute dbms_space_admin.assm_tablespace_verify(‘&tablespace_name’,dbms_space_admin.TS_VERIFY_BITMAPS)
oradebug setmypid
oradebug tracefile_name
针对不同的 analyze validate structure 后得到的结果 , 我们可以得到一些初步的结论:
如果执行 flush buffer cache之后再次analyze validate structure不再报ORA-8103错误则说明:
可能是完全正常的现象,之前的ORA-8103正是也因为对象正在被DROP/TRUNCATE而导致SELECT报ORA-8103。一般来说Call Stack会显示进程正尝试访问该段的segment header。 更多信息可以参考BUG 7441661
也可能该问题仅仅发生在buffer cache层,而没有发生在DISK上。通过flush buffer_cache若能解决,则一般是这种情况,往往是Buffer Cache管理的BUG 。
如果执行 flush buffer cache之后再次analyze validate structure再次报ORA-8103错误则说明:
如果dump对应的数据块发现 该块在逻辑上是完整一致的(也可以用bbed/dbv工具验证), 则有可能是Lost Write,则不是被其他对象重格式化使用了。
这里判断Lost Write的一个重要手段是 对块做recover/blockrecover,如果recover能修复该块,则说明是因为Lost Write引起了本ORA-8103问题,如果不是则说明99%的可能性是BUG引起的。
常见的一种现象是 使用第三方工具在数据库打开的情况下copy 数据库,这些工具的BUG可能导致copy 老的版本的block到目标新库中。
另一种可能是 extent盘区级别的不一致。 同一个数据块/extent 可能 同时属于 2个数据段segment,这导致其中的一个被后者覆盖。 通过recover的方式是无法修复这种场景的, 因为这种逻辑的讹误发生在表空间级别的extent信息上。 可以检查dba_extents/dba_segments/dba_free_space这些视图来确定问题数据块到底是否同时属于多个对象, 或者 一个数据块 同时出现在dba_extents/dba_segments/dba_free_space 三个视图中, 因为 used extent 不该出现在dba_free_space中,而free extent不该在dba_extents,当然要排除recyclebin中对象的影响。 绝大多数情况下这种extent逻辑不一致的现象, 被称作extent overlap , 通常是Oracle Space Management空间管理层面的BUG。
在对ORA-8103问题的诊断过程中 定位问题的OBJD异常重要。应当说准确地将ORA-8103错误与BUG定位起来是有难度的,因为这往往需要涉及到redo dump以发现到底是哪些opcode造成了后续的objd 或 block type 不一致。在一些BUG中我们发现,由于可能的变量陈旧,造成objd的结构未合理清除, 之后就发现block上的objd是错的了,可能遇到ORA-8103也可能是ORA-1410, 这引起了后续其他的逻辑讹误,以至于很难通过TRACE/REDO LOG DUMP来定位原始问题所在。 这也是为什么虽然在例如版本10.2.0.4上有几个ORA-8103的bug Note, 但这些BUG最终未被close为real software bug即真的软件BUG , 大多都是不了了之,因为在用户现场的TRACE和REDO DUMP都未必能真实定位到问题所在,这也是为什么我们要说逻辑讹误的分析和处理原要比物理讹误来的复杂。
Maclean的经验是 在有大量Oracle DB的环境下 一年出个几次的逻辑/物理坏块是很正常的事情, 对于物理讹误 我们只要切实备份即可99%得解决。 而对于逻辑坏块可做的 事情不多, 打最新的补丁 开 db_block_checking、db_block_checksum几件事情而已。
值得一说的是 如果去读一下ORA-8103的一些Bug Note,可以发现使用 LOB、APPEND INSERT、PARALLEL INSERT、exchange partition 、Split partition、advanced compression、HCC 混合列压缩往往是引起ORA-8103的高危操作 , 但实际我们又不可能放弃上述操作。
目前已知ORA-8103相关的BUG 列表:
| NB | Bug | Fixed | Description |
| 13910420 | 11.2.0.3.BP09, 12.1.0.0 | ORA-8103 during insert / update of basicfile LOB in assm segment using space search cache | |
| 13725395 | 11.2.0.3.BP07, 11.2.0.4, 12.1.0.0 | ORA-600 [kdzhFindHeadPiece: unnewed > 1] from load into HCC table | |
| 13700577 | 11.2.0.3.BP07, 11.2.0.4, 12.1.0.0 | PQ slave dies with ORA-600 [kdblddr_2] | |
| 12747437 | 12.1.0.0 | ORA-600 [ktspfmdb:objdchk_kcbnew_3] after purging single consumer queue table | |
| 12582839 | 11.2.0.3, 12.1.0.0 | ORA-8103/ORA-600 [3020] on RMAN recovered locally managed tablespace | |
| 12321309 | 12.1.0.0 | ORA-600 / ORA-8103 UNUSABLE state of partitioned index is not carried across by TABLESPACE transport using DataPump | |
| 11937253 | 11.2.0.2.6, 11.2.0.2.BP11, 11.2.0.3, 12.1.0.0 | A Parallel query fails with ORA-8103 on an Active Dataguard Enviroment. | |
| 11850492 | 11.2.0.3, 12.1.0.0 | ORA-8103 ORA-600 ORA-3113 on temporary tables using INDEX FAST FULL SCAN and DIRECT read | |
| 10385812 | 11.2.0.3, 12.1.0.0 | ORA-1410 or ORA-8103 by queries with DIRECT READ while concurrent DIRECT INSERT | |
| 10329146 | 11.2.0.1.BP10, 11.2.0.2.2, 11.2.0.2.BP03, 11.2.0.2.GIBUNDLE02, 11.2.0.2.GIPSU02, 11.2.0.3, 12.1.0.0 | Lost write in ASM with multiple DBWs and a disk is offlined and then onlined | |
| + | 10209232 | 11.1.0.7.7, 11.2.0.1.BP08, 11.2.0.2.1, 11.2.0.2.BP02, 11.2.0.2.GIBUNDLE01, 11.2.0.3, 12.1.0.0 | ORA-1578 / ORA-600 [3020] Corruption. Misplaced Blocks and Lost Write in ASM |
| 10136415 | 11.2.0.3, 12.1.0.0 | ORA-8103 on Partitioned IOT after partition maintenance | |
| 9965085 | 11.2.0.3, 12.1.0.0 | ORA-1578 / ORA-8103 Temporary table block corruption / space wastage from PDML | |
| 9659614 | 10.2.0.5.3, 11.2.0.2, 11.2.0.3.5, 11.2.0.3.BP05, 12.1.0.0 | Large trace file for ORA-8103 | |
| 9651350 | 11.2.0.2.2, 11.2.0.2.BP05, 11.2.0.3, 12.1.0.0 | Large redo dump and ORA-308 might be raised due to ORA-8103 | |
| 9275027 | 11.2.0.2, 12.1.0.0 | ORA-600 [kcbnew_3] can occur after TRUNCATE / DROP | |
| 9272086 | 11.1.0.7.4, 11.2.0.1.2, 11.2.0.1.BP06, 11.2.0.2, 12.1.0.0 | ORA-8103 by a query on DBA_EXTENTS. Trace file with Block type: 0x44=NGLOB: Extent Map | |
| 8754670 | 11.2.0.2, 12.1.0.0 | IMP-17 / ORA-8103 transporting a large dictionary managed tablespace | |
| 8740993 | 11.1.0.7.8, 11.2.0.2, 12.1.0.0 | ORA-1410 / ORA-8103 on ADG STANDBY during table scan after DROP/TRUNCATE/SHRINK in PRIMARY | |
| 8725282 | 11.2.0.1.BP08, 11.2.0.2, 12.1.0.0 | Corruption from cross platform transport of tablespace with securefile objects | |
| 8716064 | 11.2.0.2, 12.1.0.0 | Analyze Table Validate Structure fails on ADG standby with several errors | |
| + | 8597106 | 11.2.0.1.BP06, 11.2.0.2, 12.1.0.0 | Lost Write in ASM when normal redundancy is used |
| 8428523 | 11.2.0.2, 12.1.0.0 | Alter Table Rename causes wrong results/ora-8103/hangs on ADG Standby. | |
| 7710827 | 11.2.0.2, 12.1.0.0 | Index rebuild or Merge partition causes wrong results in concurrent reads instead of ORA-8103 | |
| 7519406 | 10.2.0.5.1, 11.2.0.1.2, 11.2.0.1.BP06, 11.2.0.2, 12.1.0.0 | Larger trace than needed for ORA-8103 under kteinicnt1 | |
| P | 12330911 | 12.1 | EXADATA LSI firmware for lost writes |
| 8876094 | 11.1.0.7.2, 11.2.0.2 | ORA-8103 by DBA_UNDO_EXTENTS or DBMS_SPACE_ADMIN.TABLESPACE_VERIFY on Block type: 0x25 | |
| 9167831 | 11.2.0.2 | ORA-8103 instead of ORA-1410 | |
| 7650993 | 11.1.0.7.1, 11.2.0.1 | ORA-8103 in a select at ADG standby database from table stored in ASSM tablespace | |
| 7432556 | 11.1.0.7.1, 11.2.0.1 | ORA-8103 by Parallel Query on Partitioned Tables in BIGFILE Tablespaces | |
| 7390324 | 11.2.0.1 | ANALYZE signals OERI [kcbgtcr_12]/ORA-8103 on bitmap index | |
| 7117200 | 11.2.0.1 | ORA-8103 after TSPITR/PLUGIN tablespace from a restored Level 1 Backup | |
| 8825048 | 11.1.0.7.3 | ORA-308/ORA-27037 when dumping archived log for ORA-8103. Dump when event 10736 level 4 is set | |
| 6337376 | 11.1.0.7 | OERI:kcbgcur_3 / ORA-8103 after truncating a partition table with LOBs | |
| 9711472 | 11.1.0.6 | ORA-8103 on operations for a partitioned LOB if any different partition is dropped | |
| 5637976 | 10.2.0.4, 11.1.0.6 | ORA-8103/ORA-1410 from concurrent INSERT / export on ASSM tables | |
| 5083393 | 10.2.0.4, 11.1.0.6 | DBA_FREE_SPACE FILE_ID / REL_FNO may be wrong | |
| 4592596 | 10.2.0.4, 11.1.0.6 | Corruption (ORA-1410 / ORA-8103) from multi-table insert with direct load | |
| 6864586 | 10.2.0.5 | ORA-8103 on partitioned table with a LOB column during analyze table with concurrent add/drop partition. | |
| 3569503 | 9.2.0.6, 10.2.0.4 | PQ may signal a false ORA-8103 under load | |
| 13618170 | ORA-8103 for create index online when the fix of bug 10027403 is installed | ||
| 3966709 | 9.2.0.7, 10.1.0.4, 10.2.0.1 | Range/object reuse prematurely (ORA-8103) | |
| 3868753 | 9.2.0.7, 10.1.0.5, 10.2.0.1 | Concurrent export / INSERT of ASSM segment can fail with ORA-1410 / ORA-8103 | |
| + | 5523799 | Various OERI (eg kcbgtcr_12) using ASSM managed segments – superceded | |
| P* | 6047085 | Linux x64-64: SGA corruption / crash following any ORA-7445 | |
| * | 3785200 | 9.2.0.6, 10.1.0.2 | Corruption possible in automatic space managed segments |
| 3083560 | 9.2.0.5, 10.1.0.2 | ORA-1410 / ORA-8103 from direct path export if concurrent DML occurs | |
| 2619867 | 9.2.0.3, 10.1.0.2 | OERI:[KCBGTCR_12] / ORA-8103 / ORA-1410 SELECTing from bitmap managed segment | |
| 2551000 | 9.2.0.4, 10.1.0.2 | False ORA-1410 / ORA-8103 possible from ANALYZE COMPUTE/ESTIMATE STATISTICS | |
| 2333731 | 9.2.0.2 | ORA-8103 possible in PQ slave | |
| 2105419 | 9.0.1.3, 9.2.0.1 | ORA-8103 possible from PQ on bitmap managed segments with concurrent inserts | |
| 1998455 | 8.1.7.3, 9.0.1.3, 9.2.0.1 | OERI:KCBGTCR_4 possible from long running DDL if referenced object dropped/truncated | |
| 1804299 | 9.0.1.1, 9.2.0.1 | Rollback of Direct load can corrupt BITMAP managed segments / ORA-8103 | |
| 1698789 | 9.2.0.1 | Wrong results, ORA-1410, ORA-8103, OERI:25012 on SELECT of UNSCOPED REF with ROWID | |
| 1504967 | 9.2.0.1 | ORA-8103 possible on READ ONLY standby after TRUNCATE on primary | |
| 1400739 | 8.1.7.1, 9.0.1.0 | Block corruption/OERI:2023 /ORA-8103 can occur if TRUNCATE is interrupted (Ctrl-C) | |
| 1283521 | 8.1.7.0 | ORA-8103 can occur on TRUNCATED cluster table | |
| 589855 | 7.3.3.6, 7.3.4.1 | ORA:1578 or ORA:8103 selecting invalid ROWID | |
| P | 1053863 | 8.0.5.2, 8.0.6.2 | NCR: ORA-8103 / corrupt read possible using async IO |
对于ORA-8103问题的更多信息可以参考:
MOS文档Note 268302.1 ORA-8103 Diagnostics and Solution
【数据恢复】利用构造ROWID实现无备份情况下绕过ORA-1578、ORA-8103、ORA-1410等逻辑/物理坏块问题