Summary
ParnassusData Recovery Manager (PRM-DUL) is an enterprise Oracle database recovery tool, which can extract database datafile from Oracle 9i, 10g, 11g, 12c directly without any SQL execution on database. ParnassusData Recovery Manager was developed by Java, which can be used cross platforms. It can be run without any installation. Download it, and click to run
PRM-DUL has full rich GUI for any command. It is not necessary to learn script or master any skill in Oracle data structure. Recovery Wizard is integrated in the tool.
Download PRM-DUL: https://zcdn.parnassusdata.com/DUL5108.zip
Why PRM-DUL is necessary?
Isn’t RMAN enough for ORACLE database recovery? Why need PRM-DUL for Oracle recovery?
In modern growing IT systems, database size is growing geometrically. Oracle DBAs are facing the problem that disks are insufficient for full backup, and tape storages take much more time than usual expectation.
Truth been told, “Database, backup 1st” is the first lesson for DBAs, however that fact is : disk space is not sufficient, new storage is still on the way, even the backup image may not work.
In order to solve the above problems, PD Recovery Manager integrates the algorithm in Oracle database data structure, boot process which can solve system table lost, data dictionary error, and storage corruption impaction. In addition, it can also recovery the data from Truncate/DROP mistake.
No matter you are a professional DBA or new fish in Oracle world, you can master this user-friendly tool immediately. PRM-DUL is easy to install and use. You don’t need to have any Oracle deep knowledge or skill in scripts, but just click-by-click finishing all recovery process.
Comparing the traditional recovery tool like Oracle DUL that is an Oracle internal tool and only for Oracle employee usage. PRM-DUL can be used for any kind of IT professionals or geeks. It saves time, decreases the recovery failure, and cuts down the total cost of enterprise.
There are 2 modes for data recovery:
By traditional way, data has to be extract to text file and then insert to new DB by SQLLDR tools, which takes double time and occupies double storage size.
ParnassusData Recovery Manager integrates data bridge features, which can extract data from original source database and then insert into new destination database without any inter-media. This is a truly time and storage saver.
Oracle ASM is becoming popular in enterprise database implementation, due to its advantage in high performance, cluster support, and easy administration. However, for many IT professionals, ASM is a black box. Once ASM occurs error in disk group mounting, it means that all data is locked in ASM. In this circumstance, without PRM-DUL, only senior Oracle experts can patch ASM internal structure, which is also a problem for oracle normal user.
PRM-DUL now can support two kinds of ASM data recovery:
- Once Disk Group cannot be mounted, PRM-DUL can read metadata, and clone ASM file from Disk Group
- Once Disk Group cannot be mounted, PRM-DUL can read ASM file and extract data, which supports data export, and data bridge 2 modes
PRM-DUL Software Introduction
ParnassusData Recovery Manager (PRM-DUL) was developed by Java, which ensured cross-platform ability. No matter AIX, Solaris, HPUNIX, Red-Hat, Oracle Linux, SUSE, or Window, It can be run smoothly.
PRM-DUL Supports OS & Platform:
| Platform Name | Supported |
| AIX POWER | ü |
| Solaris Sparc | ü |
| Solaris X86 | ü |
| Linux X86 | ü |
| Linux X86-64 | ü |
| HPUX | ü |
| MacOS | ü |
PRM-DUL Supported Database Version:
| ORACLE DATABASE VERSION | Supported |
| Oracle 7 | û |
| Oracle 8 | û |
| Oracle 8i | û |
| Oracle 9i | ü |
| Oracle 10g | ü |
| Oracle 11g | ü |
| Oracle 12c | ü |
PRM-DUL runs at least on JAVA JDK 1.8. Parnassus Data strongly recommends you to run it on JDK 1.8.
PRM-DUL hardware requirement:
| CPU | At least 800 MHZ |
| Memory | At least 512 MB |
| Disk | At least 50 MB |
PRM-DUL recommended hardware requirement:
| CPU | 2.0 GHZ |
| Memory | 2 GB |
| Disk | 2 GB |
PRM-DUL Language Support
| Language | Character Set | Encoding |
| Simplified/Traditional Chinese | ZHS16GBK | GBK |
| Simplified/Traditional Chinese | ZHS16DBCS | CP935 |
| Simplified/Traditional Chinese | ZHT16BIG5 | BIG5 |
| Simplified/Traditional Chinese | ZHT16DBCS | CP937 |
| Simplified/Traditional Chinese | ZHT16HKSCS | CP950 |
| Simplified/Traditional Chinese | ZHS16CGB231280 | GB2312 |
| Simplified/Traditional Chinese | ZHS32GB18030 | GB18030 |
| Japanese | JA16SJIS | SJIS |
| Japanese | JA16EUC | EUC_JP |
| Japanese | JA16DBCS | CP939 |
| Korean | KO16MSWIN949 | MS649 |
| Korean | KO16KSC5601 | EUC_KR |
| Korean | KO16DBCS | CP933 |
| French | WE8MSWIN1252 | CP1252 |
| French | WE8ISO8859P15 | ISO8859_15 |
| French | WE8PC850 | CP850 |
| French | WE8EBCDIC1148 | CP1148 |
| French | WE8ISO8859P1 | ISO8859_1 |
| French | WE8PC863 | CP863 |
| French | WE8EBCDIC1047 | CP1047 |
| French | WE8EBCDIC1147 | CP1147 |
| Deutsch | WE8MSWIN1252 | CP1252 |
| Deutsch | WE8ISO8859P15 | ISO8859_15 |
| Deutsch | WE8PC850 | CP850 |
| Deutsch | WE8EBCDIC1141 | CP1141 |
| Deutsch | WE8ISO8859P1 | ISO8859_1 |
| Deutsch | WE8EBCDIC1148 | CP1148 |
| Italian | WE8MSWIN1252 | CP1252 |
| Italian | WE8ISO8859P15 | ISO8859_15 |
| Italian | WE8PC850 | CP850 |
| Italian | WE8EBCDIC1144 | CP1144 |
| Thai | TH8TISASCII | CP874 |
| Thai | TH8TISEBCDIC | TIS620 |
| Arabic | AR8MSWIN1256 | CP1256 |
| Arabic | AR8ISO8859P6 | ISO8859_6 |
| Arabic | AR8ADOS720 | CP864 |
| Spanish | WE8MSWIN1252 | CP1252 |
| Spanish | WE8ISO8859P1 | ISO8859_1 |
| Spanish | WE8PC850 | CP850 |
| Spanish | WE8EBCDIC1047 | CP1047 |
| Portuguese | WE8MSWIN1252 | CP1252 |
| Portuguese | WE8ISO8859P1 | ISO8859_1 |
| Portuguese | WE8PC850 | CP850 |
| Portuguese | WE8EBCDIC1047 | CP1047 |
| Portuguese | WE8ISO8859P15 | ISO8859_15 |
| Portuguese | WE8PC860 | CP860 |
Features Supported
| Features | Supported |
| Cluster Table | YES |
| Inline or out-of-line LOBS, different chunk version and size, LOB partition | YES |
| Heap table, partitioned or non-partitioned | YES |
| Partition and Subpartition | YES |
| Table With chained rows ,migrated rows,intra-block chaining | YES |
| Bigfile Tablespace | YES |
| ASM Automatic Storage Management 10g,11g,12c,diskgroups are dismounted | YES |
| ASM 11g Variable Extent Size | YES |
| IOT, partitioned or non-partitioned | YES(Future) |
| Basic Compressed Heap table | YES(Future) |
| Advanced Compressed Heap Table | NO |
| Exudates HCC Heap Table | NO |
| Encrypted Heap Table | NO |
| Table with Virtual Column | NO |
Attention: for virtual column、11g optimized default column, it may lose some column, and these two are new feature and less used in production environment.
PRM-DUL supports data type:
| Data Type | Supported |
| BFILE | No |
| Binary XML | No |
| BINARY_DOUBLE | Yes |
| BINARY_FLOAT | Yes |
| BLOB | Yes |
| CHAR | Yes |
| CLOB and NCLOB | Yes |
| Collections (including VARRAYS and nested tables) | No |
| Date | Yes |
| INTERVAL DAY TO SECOND | Yes |
| INTERVAL YEAR TO MONTH | Yes |
| LOBs stored as SecureFiles | Future |
| LONG | Yes |
| LONG RAW | Yes |
| Multimedia data types (including Spatial, Image, and Oracle Text) | No |
| NCHAR | Yes |
| Number | Yes |
| NVARCHAR2 | Yes |
| RAW | Yes |
| ROWID, UROWID | Yes |
| TIMESTAMP | Yes |
| TIMESTAMP WITH LOCAL TIMEZONE | Yes |
| TIMESTAMP WITH TIMEZONE | Yes |
| User-defined types | No |
| VARCHAR2 and VARCHAR | Yes |
| XMLType stored as CLOB | No |
| XMLType stored as Object Relational | No |
PRM-DUL supports ASM:
| Function | Supported |
| Directly extract Table data from ASM | YES |
| Directly copy datafile from ASM | YES |
| Repair ASM metadata | YES |
| Draw ASM Structure by GUI | Future |
PRM-DUL installation and boot
It is not necessary to install PRM-DUL since it is Java developed software. Extract the ZIP package and click to RUN
| unzip PRM-DUL_latest.zip |
ParnassusData recommends you to run PRM-DUL with command line, therefore it will show more diagnose information
Windows:
- Make sure you had installed JDK and add JAVA to profile
- Double click ‘PRM-DUL.bat’ which is in the folder
PRM-DUL.bat will launch PRM-DUL in the back
Then, it pops up PRM-DUL main interface:
Linux/Unix:
In Linux/Unix, use X Server for GUI
- Make sure you had installed JDK and add Java to profile
- cd to PRM-DUL folder, and run./PRM-DUL.sh to start the tool
PRM-DUL License Registration
ParnassusData Recovery Manager (PRM-DUL) needs license for full use. ParnassusData provide community version for user testing and demo. (Community version has no limits on ASM clone, and we will add more function on it)
User can purchase license via office website: www.parnassusdata.com, and it needs Database name. After your purchasing, you will receive an email which includes DBNAME and License Key
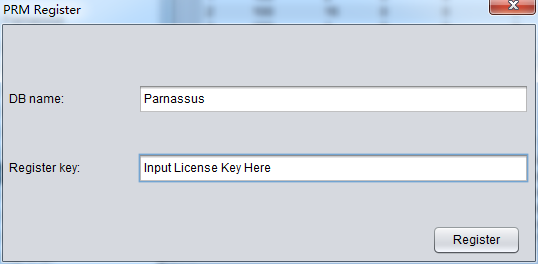
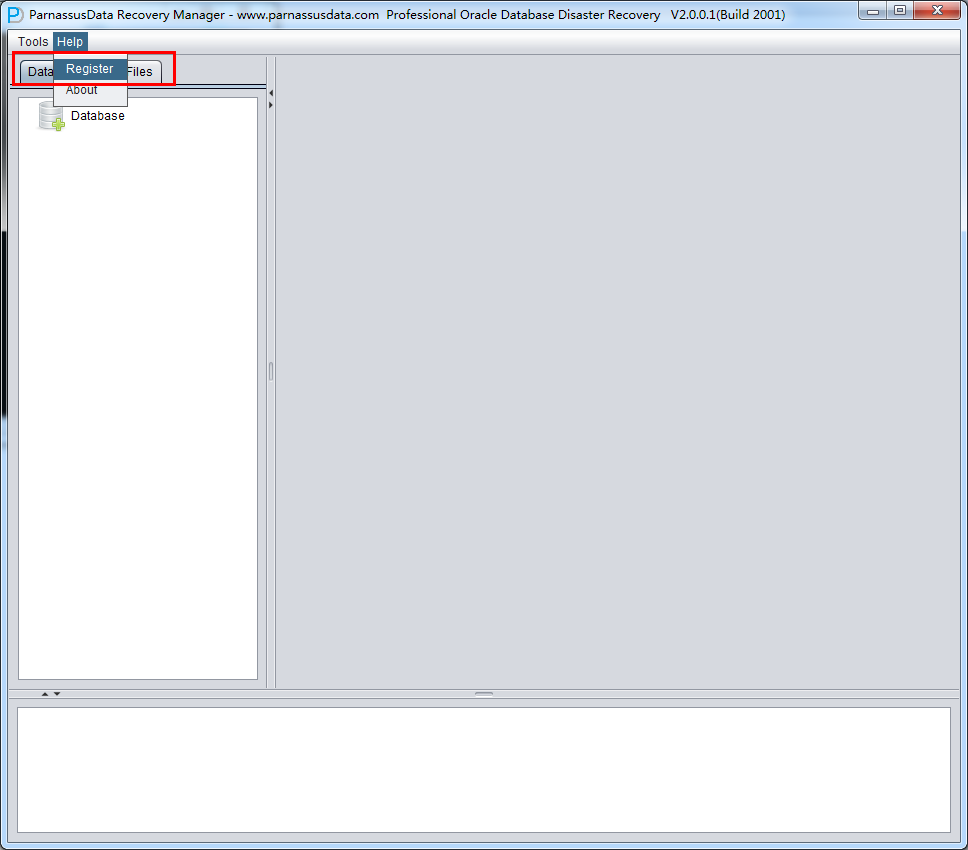
Once you have License Key, please register the software as below;
Menu Help => Register
Input DB NAME and you License Key, then click Register button
After registration, you don’t need to input license key again on your next boot.
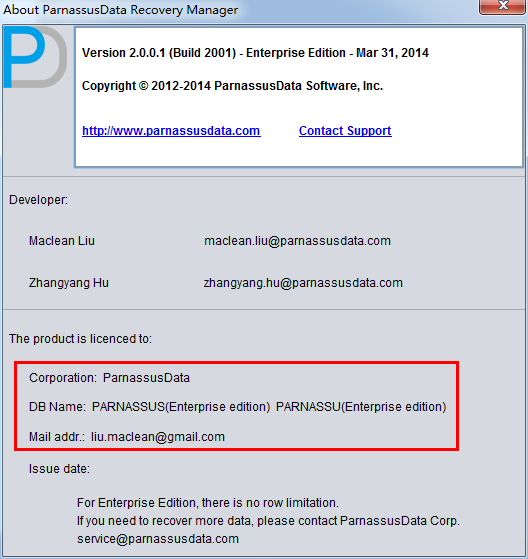
Your successful registration information is in Help=>about
Case Study on Oracle database recovery via PRM-DUL
CASE 1: Truncate table by mistake
User D had truncated a table by mistake on production environment. The DBA tried to recover table from RMAN backup, and accidently the backup is unavailable. Therefore DBA decided to use PRM-DUL for rescuing all truncated data.
Since all database system files are healthy, DBA just needs to load SYSTEM table data file in dictionary mode and TRUNCATED table file. For example:
| create table ParnassusData.torderdetail_his1 tablespace users asselect * from parnassusdata.torderdetail_his;
|
Run PRM-DUL, and select Tools =>Recovery Wizard
Click Next
Client did not user ASM storage, therefore just select ‘Dictionary Mode’:
Next, we need to select some characters: including Endian bit order and DBNAME
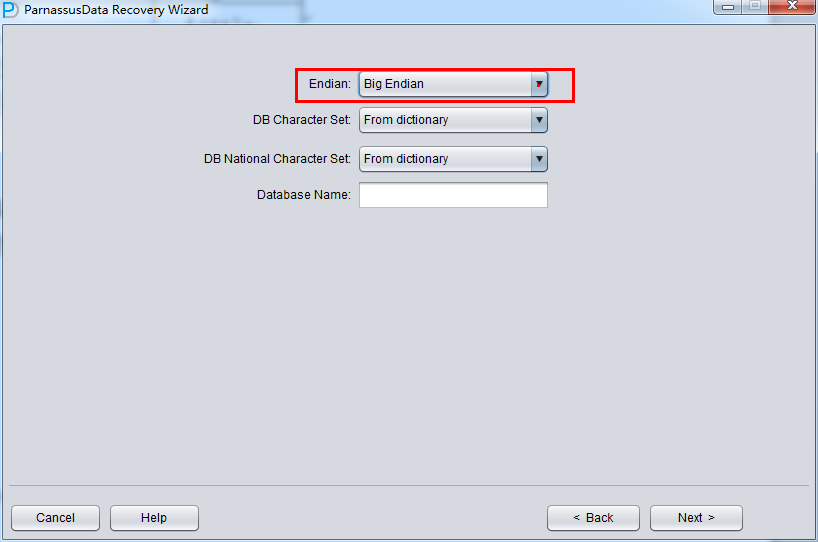
Since Oracle datafiles have different Endian bit orders on different OS, please choose accordingly:
| Solaris[tm] OE (32-bit) | Big |
| Solaris[tm] OE (64-bit) | Big |
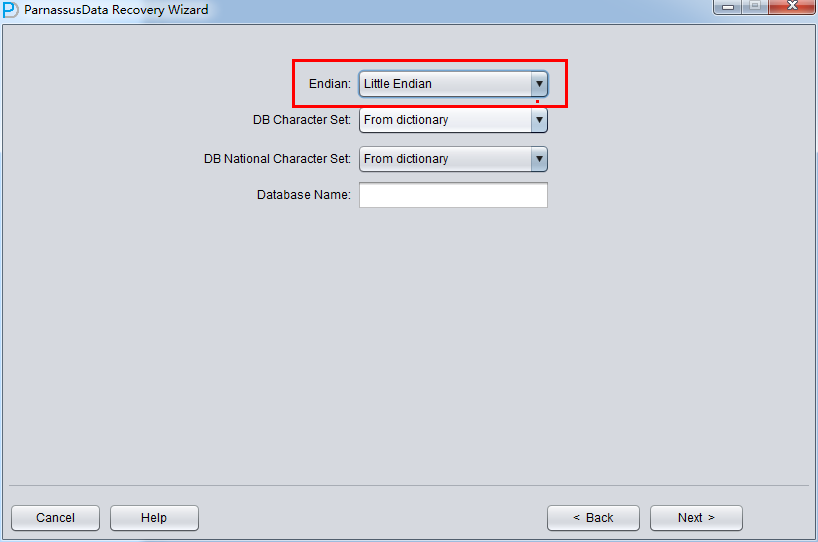
| Microsoft Windows IA (32-bit) | Little |
| Linux IA (32-bit) | Little |
| AIX-Based Systems (64-bit) | Big |
| HP-UX (64-bit) | Big |
| HP Tru64 UNIX | Little |
| HP-UX IA (64-bit) | Big |
| Linux IA (64-bit) | Little |
| HP Open VMS | Little |
| Microsoft Windows IA (64-bit) | Little |
| IBM zSeries Based Linux | Big |
| Linux x86 64-bit | Little |
| Apple Mac OS | Big |
| Microsoft Windows x86 64-bit | Little |
| Solaris Operating System (x86) | Little |
| IBM Power Based Linux | Big |
| HP IA Open VMS | Little |
| Solaris Operating System (x86-64) | Little |
| Apple Mac OS (x86-64) | Little |
In traditional UNIX, AIX (64-bit), UP-UNIX (64-bit), it use Big Endian bit order,
Usually, Linux X86/64, Windows remain default Little Endian:
Attention: if your data file was generated on AIX, if you want to recover data on window, please select original Big Endian format.
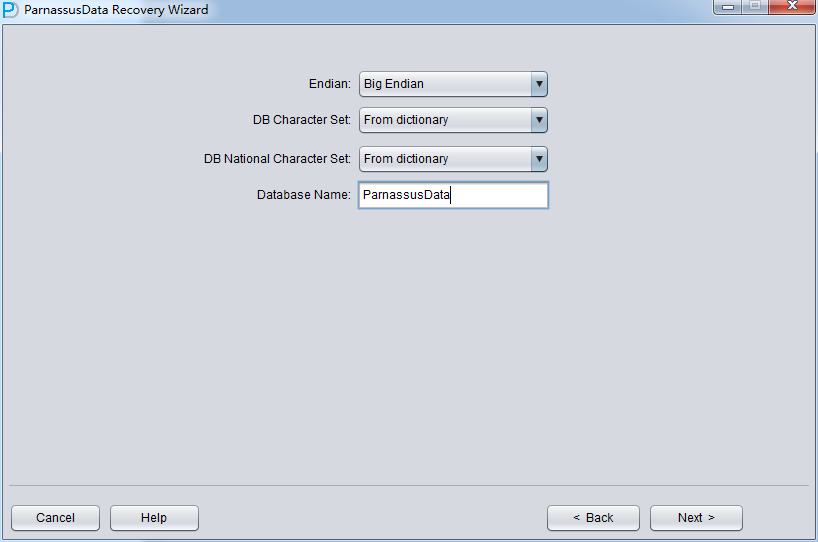
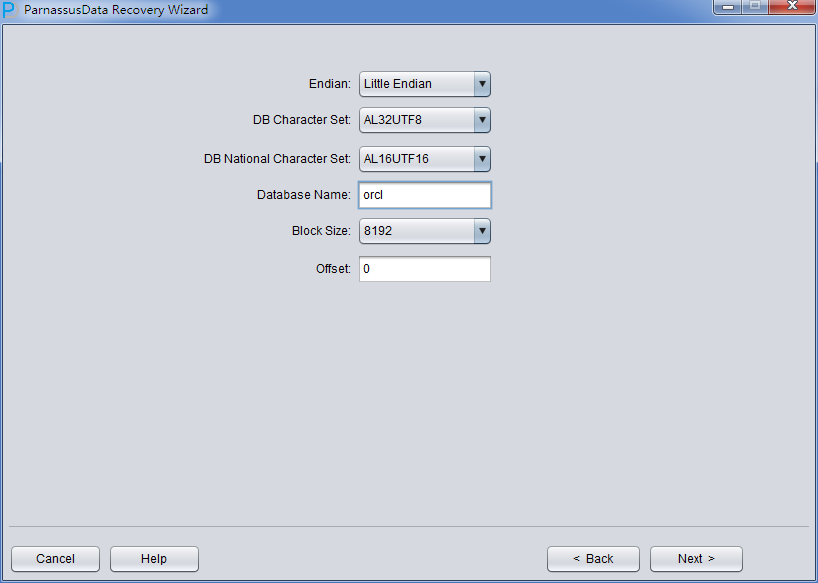
Since the data file is on Linux X86, we select Little as Endian, and input database name. (The input database name can be different from DB_NAME found in datafile header, the input database name is just an alias. PRM-DUL will check if your PRM-DUL license is valid , the valid license key is generated based on DB_NAME found in datafile header)
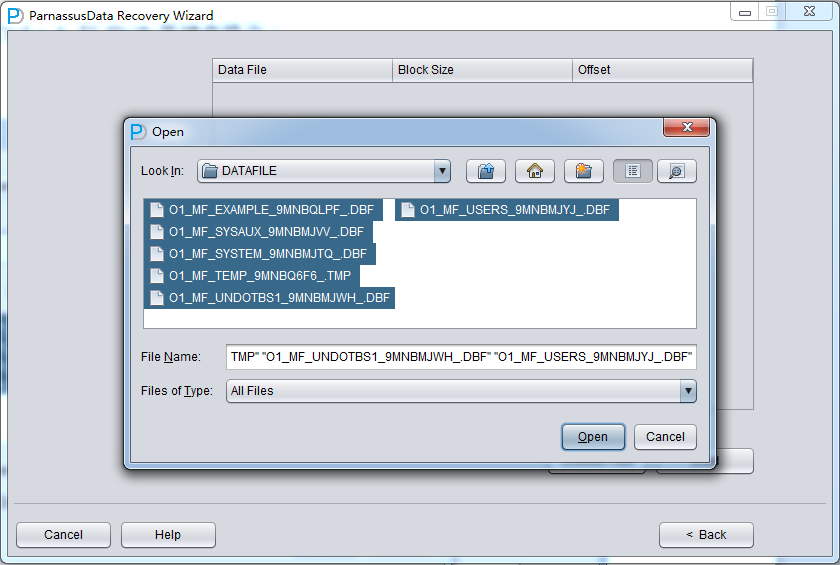
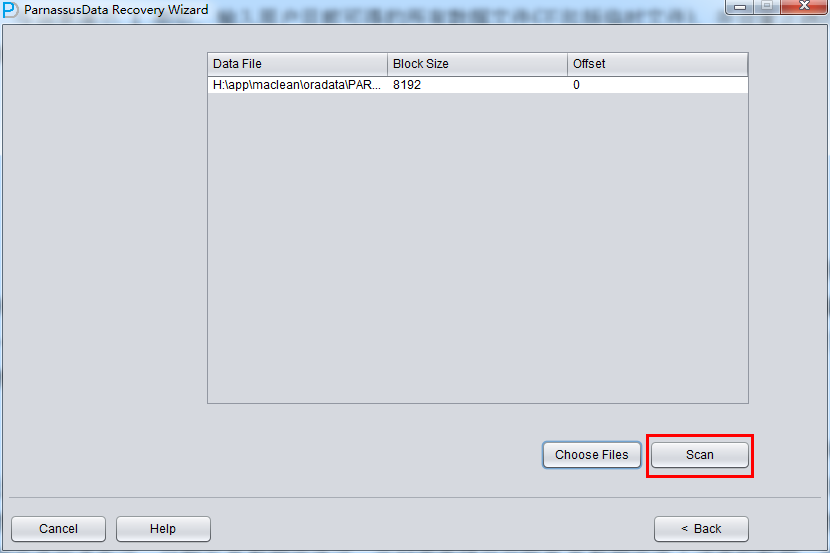
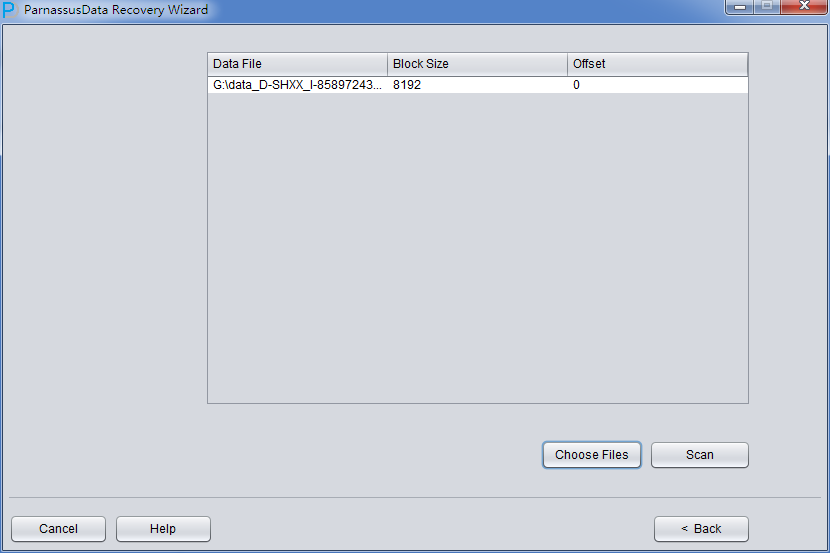
Click Next =>Click Choose Files
Usually, if the database is not too big, we could select all data files together; if the database capacity is huge and DBA knows the data location, at least you should select both SYSTEM tablespace and specified datafile.
Attention, the GUI Supports Ctrl + A & Shift short keys:
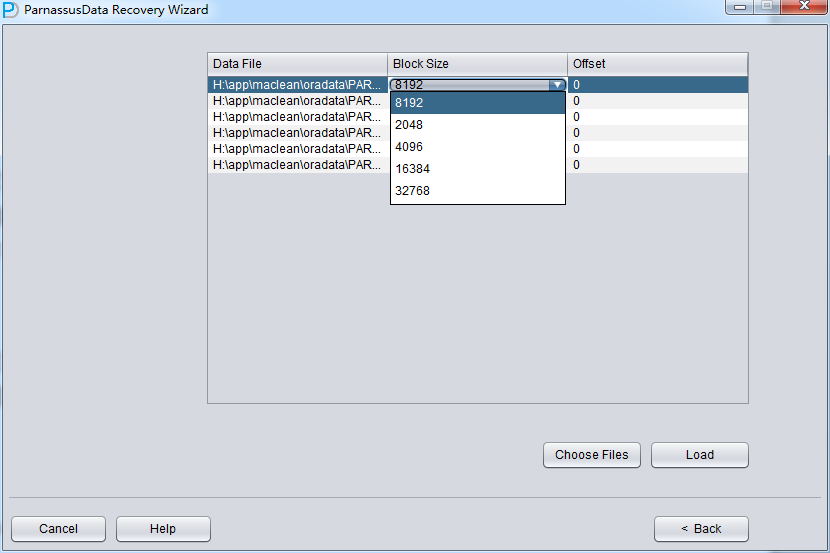
Specify the Block Size (Oracle data block size) according to the real circumstance. For example, if default DB_BLOCK_SIZE is 8K, but part of tablespaces’ block size is 16k,then user has to specify them as correct block size one by one.
OFFSET setting are just for raw device storage mode, for example: on AIX, based on LV of normal VG, the offset will be 4k OFFSET.
If you are using raw device but don’t know what the OFFSET is, please use dbfsize tool which is under $ORACLE_HOME/bin
| $dbfsize /dev/lv_control_01Database file: /dev/lv_control_01Database file type: raw device without 4K starting offsetDatabase file size: 334 16384 byte blocks |
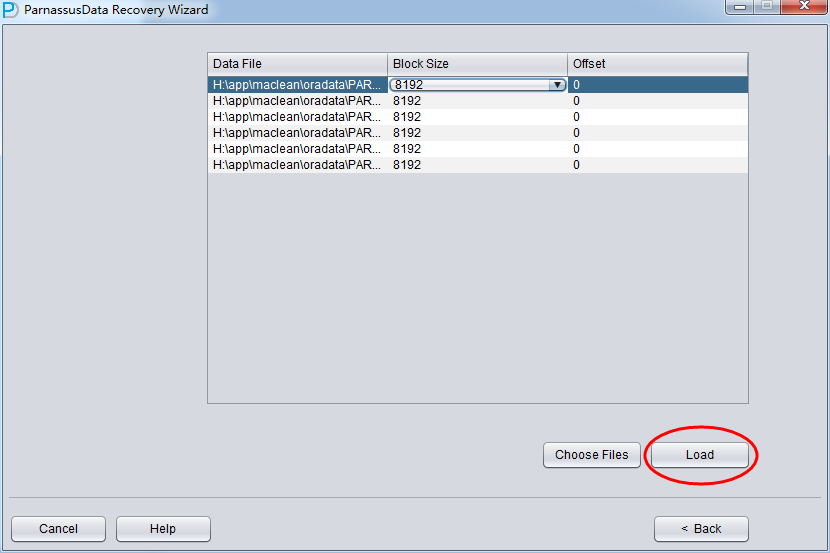
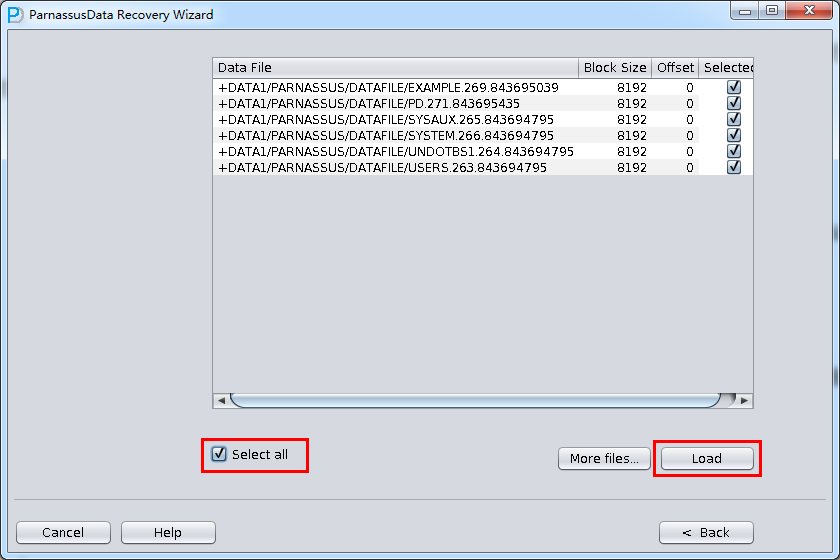
Since all data file block size here is 8K and there is no OFFSET, please click load:
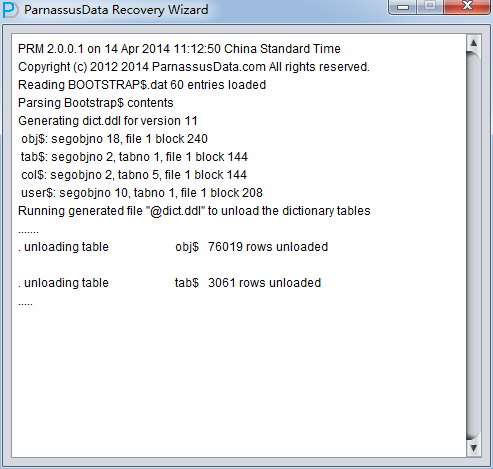
PRM-DUL read Oracle dictionary directly, and recreate a new dictionary in embedded database. It can help us to recuse most types of data in Oracle DB.
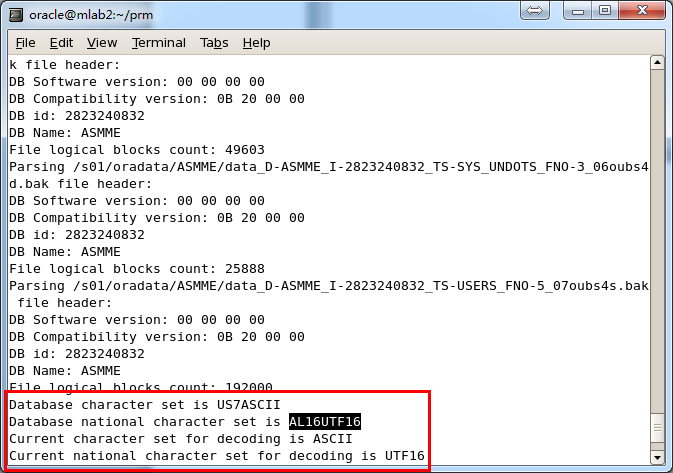
After recreating dictionary, the dialog show character information:
Attention: PRM-DUL supports multiple languages and multiple Oracle character set. However, the prerequisite is the OS had installed specified language packages. For example, on Windows, if you didn’t install Chinese language package, even Oracle database characters are independent and support ZHS16GBK, PRM-DUL would display Chinese as messy code. Once the Chinese language package is installed on OS, PRM-DUL can display multibyte character set properly.
Similarly, on Linux, it need font-Chinese language package.
| [oracle@mlab2 log]$ rpm -qa|grep chinesefonts-chinese-3.02-12.el5 |
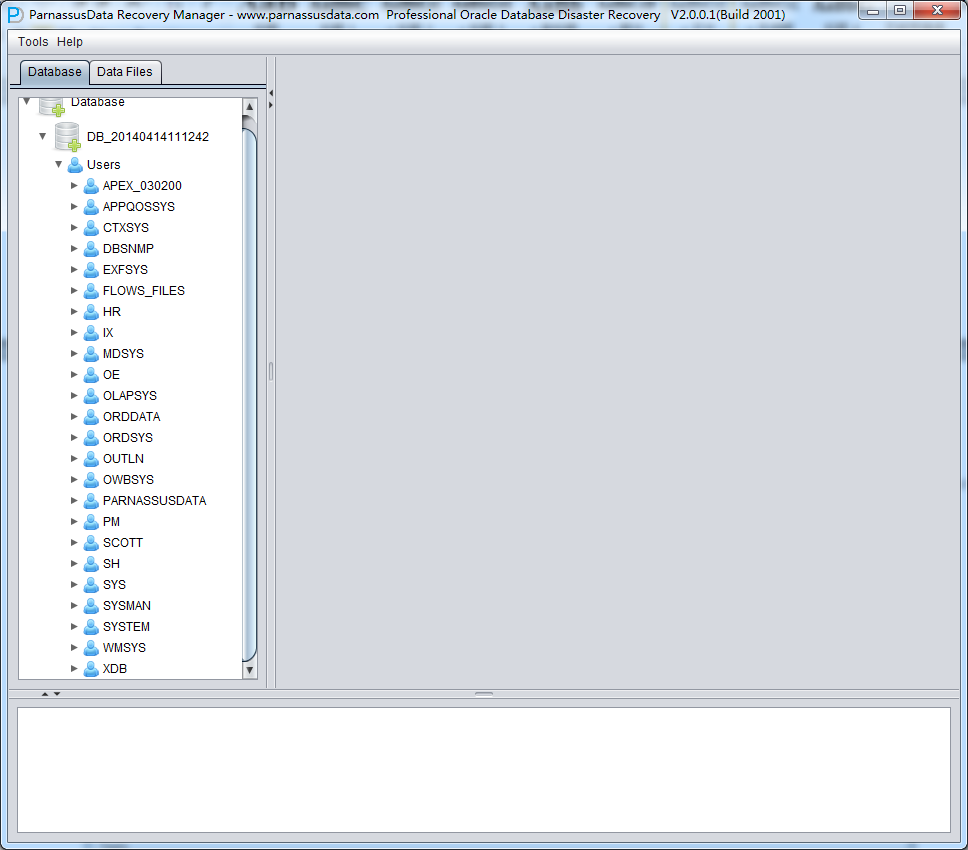
After loading, in PRM-DUL GUI, it displayed database tree diagram by database users.
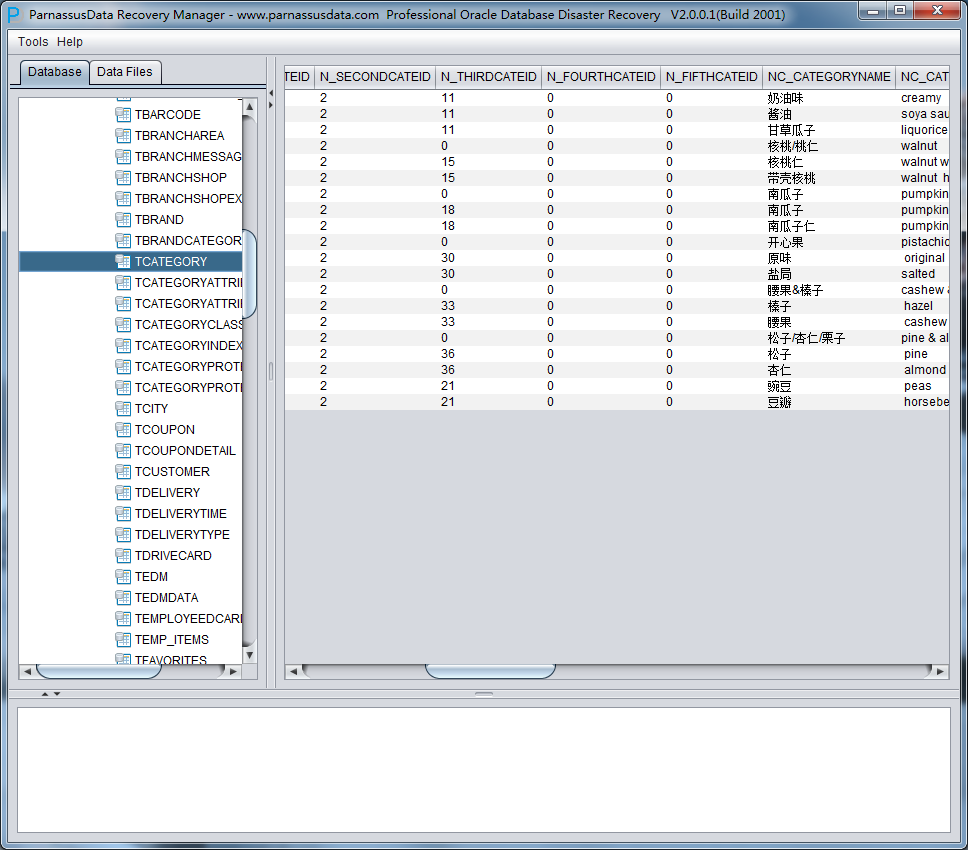
Click Users, you can find more users, for example, if user want to recover a table under PARNASSUSDATA SCHEMA, click PARNASSUSDATA, and double click that table:
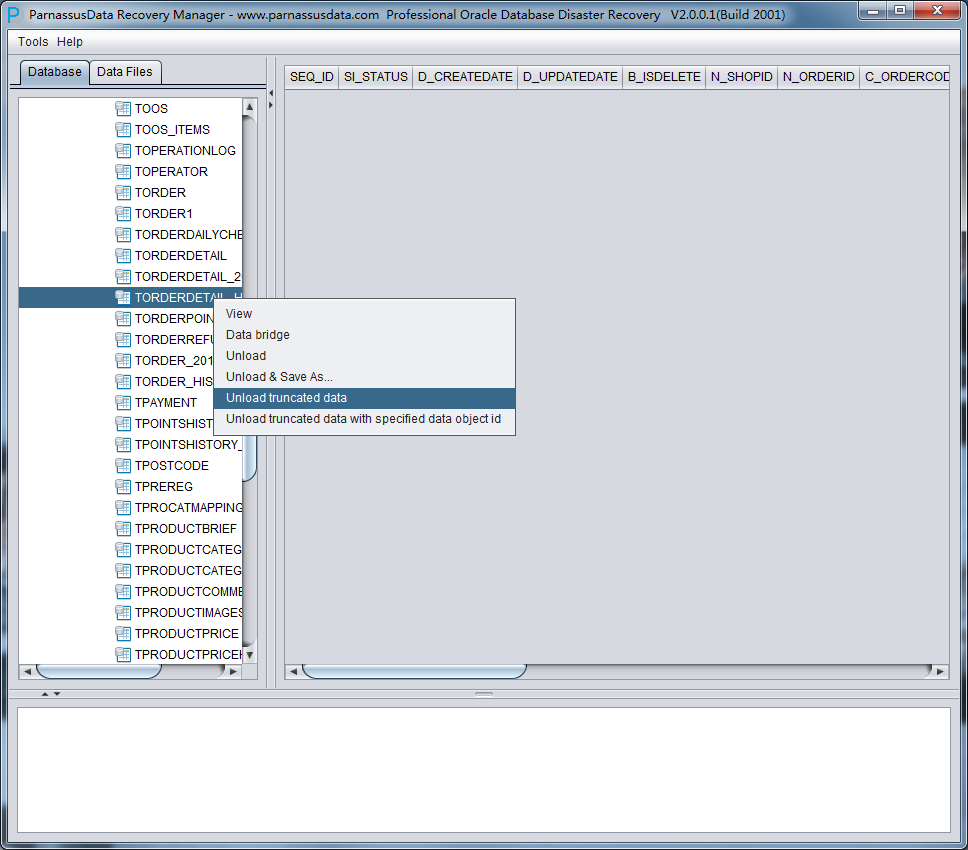
Previously TORDERDETAIL_HIS had been truncated, so it won’t show any data . Please select unload truncated Data:
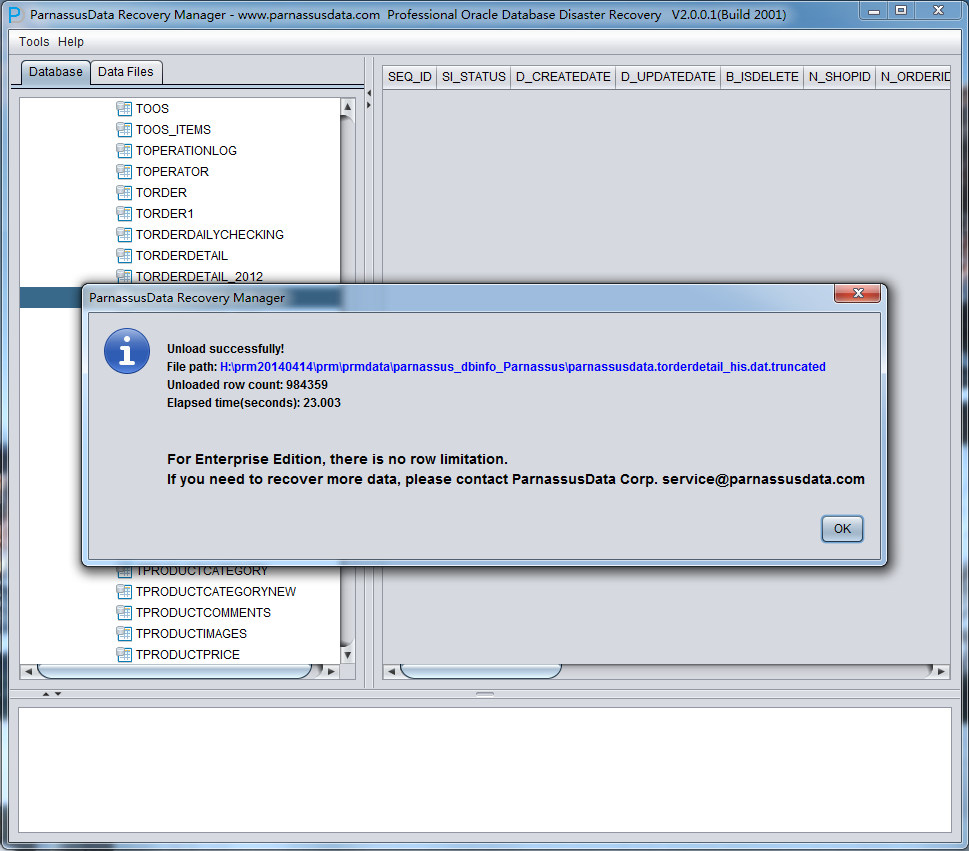
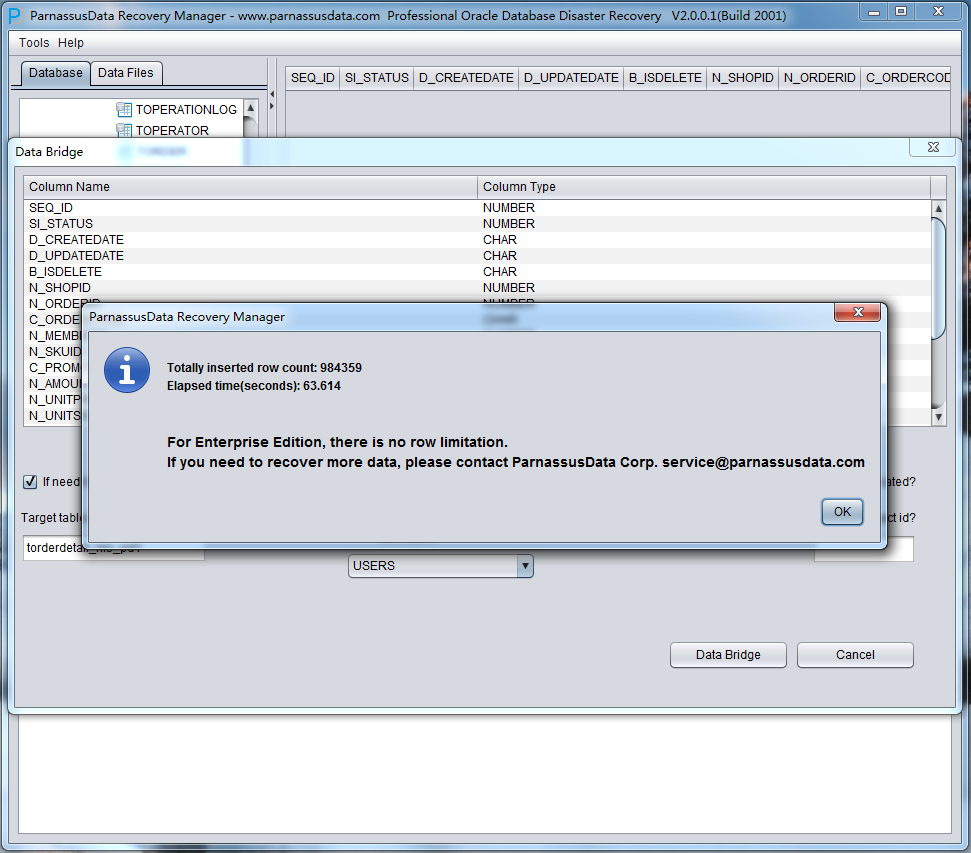
PRM-DUL will scan the tablespace and extract data from truncated table.
As in the above picture, the truncated TORDERDETAIL_HIS had exported 984359 record, and saved to specified falt file.
In addition, it generated SQLLDR control file for text data importing
| $ cd /home/oracle/PRM-DUL/PRM-DULdata/parnassus_dbinfo_PARNASSUSDATA/$ ls -l ParnassusData*-rw-r–r– 1 oracle oinstall 495 Jan 18 08:31 ParnassusData.torderdetail_his.ctl-rw-r–r– 1 oracle oinstall 191164826 Jan 18 08:32 ParnassusData.torderdetail_his.dat.truncated
$ cat ParnassusData.torderdetail_his.ctl LOAD DATA INFILE ‘ParnassusData.torderdetail_his.dat.truncated’ APPEND INTO TABLE ParnassusData.torderdetail_his FIELDS TERMINATED BY ‘ ‘ OPTIONALLY ENCLOSED BY ‘”‘ TRAILING NULLCOLS ( “SEQ_ID” , “SI_STATUS” , “D_CREATEDATE” , “D_UPDATEDATE” , “B_ISDELETE” , “N_SHOPID” , “N_ORDERID” , “C_ORDERCODE” , “N_MEMBERID” , “N_SKUID” , “C_PROMOTION” , “N_AMOUNT” , “N_UNITPRICE” , “N_UNITSELLINGPRICE” , “N_QTY” , “N_QTYFREE” , “N_POINTSGET” , “N_OPERATOR” , “C_TIMESTAMP” , “H_SEQID” , “N_RETQTY” , “N_QTYPOS” )
|
When you import data to original table, ParnassusData strongly recommends you to modify SQLLDR table name as a temp table, it would not impact your previous environment.
| $ sqlldr control=ParnassusData.torderdetail_his.ctl direct=yUsername:/ as sysdba//user SQLLDR to import data
//Minus can be used for data comparing select * from ParnassusData.torderdetail_his minus select * from parnassus.torderdetail_his;
no rows selected
|
After diffing, there is no difference between original data and PRM-DUL exported data.
PRM-DUL successfully recovered the truncated table
CASE 2: Recovery mis-truncated table by DataBridge
In Case 1, we use traditional unload+sqlldr for data recovery, but actually ParnassusData would like to strongly recommend using DataBridge Feature for recovering.
Why use DataBridge?
- Traditional unload+sqlldr means a copy of data needs to be saved as flat file on filesystem first, data has to be loaded into Unicode text file and then inserted into destination database by sqlldr, this will take double storage and double time.
- DataBridge can extract data from source DB and export to destination DB without any intermediary.
- Once the data arrived destination DB, user can begin to validate them.
- If source and destination database located on different servers, then read/write IO will be balanced on two servers , MTTR will be saved.
- If DataBridge is used in truncated table recovery, it is very convenient that truncated data can be exported back to problem database directly.
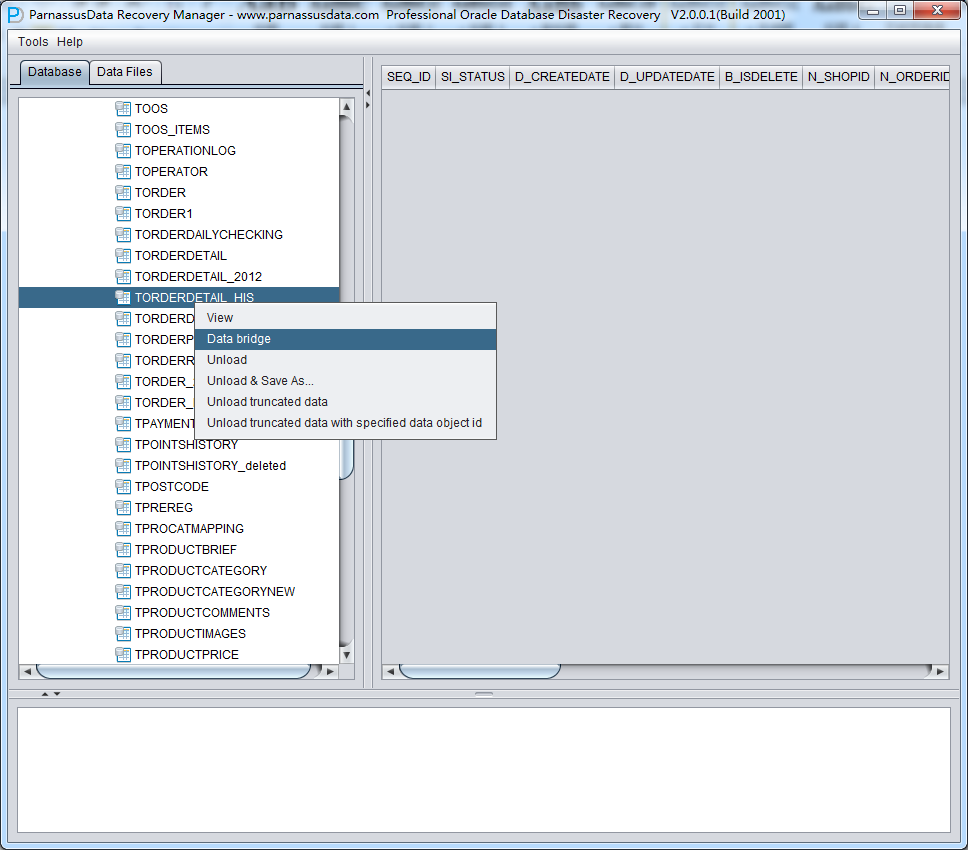
DataBridge is very simple and convenient. Right click the table on the left side, and select DataBridge:
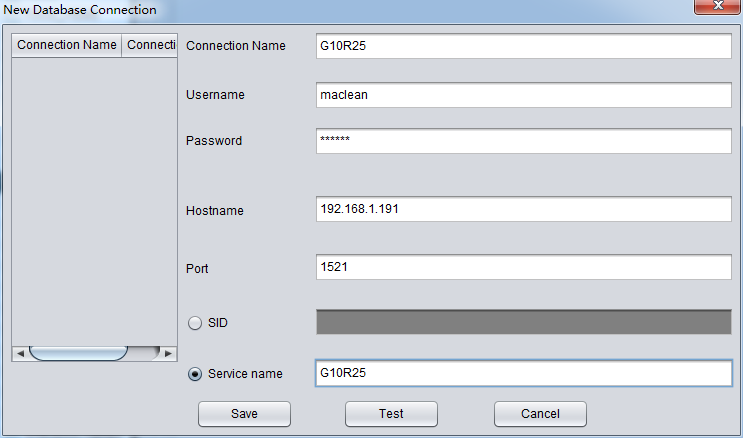
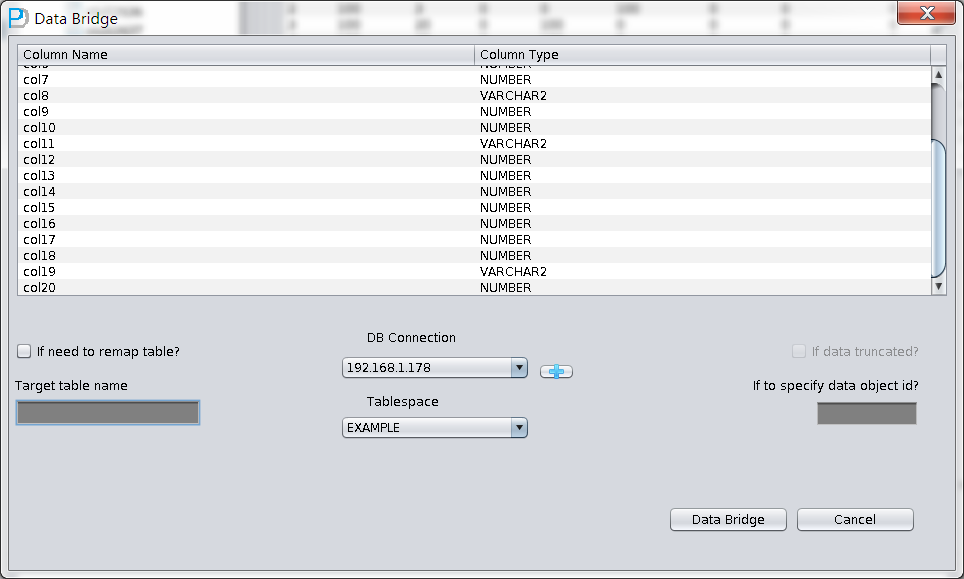
As the first time to use DataBridge, DB connection information is necessary, which is similar with SQL Developer connection, including: DB host, Port, Service_Name and Account information.
Attention: DataBridge will save data to the specified schema given in the DB connection.
AS above G10R25 connection, user is maclean, and the corresponding Oracle Easy Connection is
192.168.1.191:1521/G10R25。
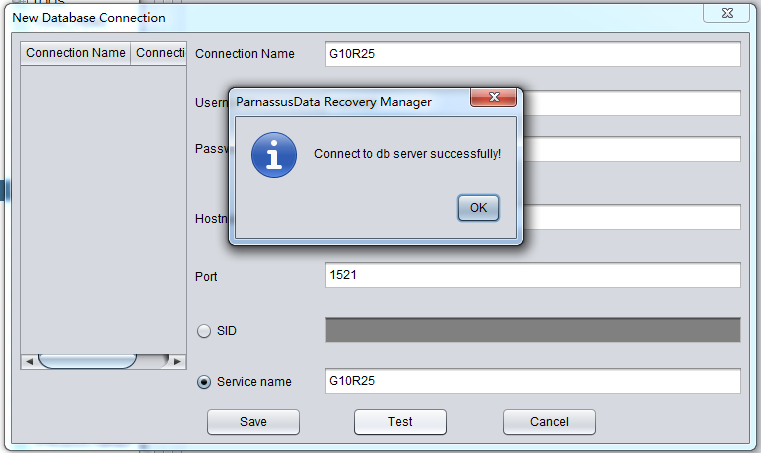
After inputting the account/connection information, you can use test for connection testing. If return message is “ Connect to DB server successfully “, the connection is done and click to save.
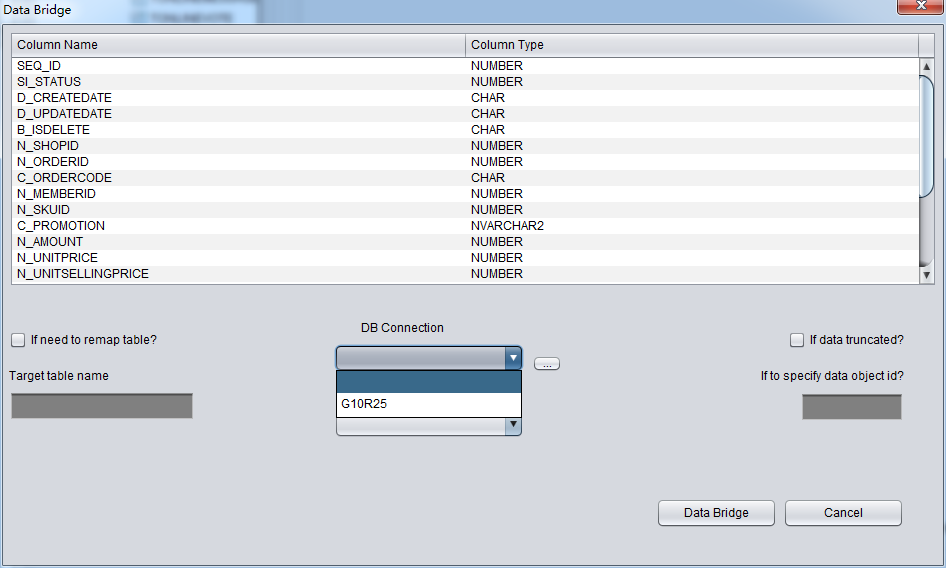
After saving connection and go to DataBridge window, please select Connection G10R25 at the drop down list.
If your DB connection is not in the drop down list, please click DB connection Button, which is highlighted in red.
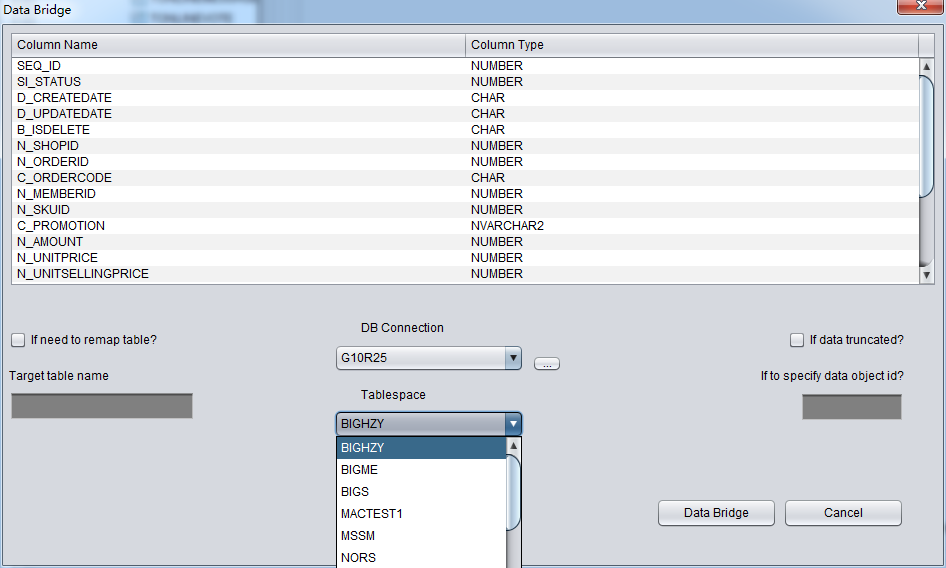
After selecting DB Connection, Tablespace dropdown list will be selectable:
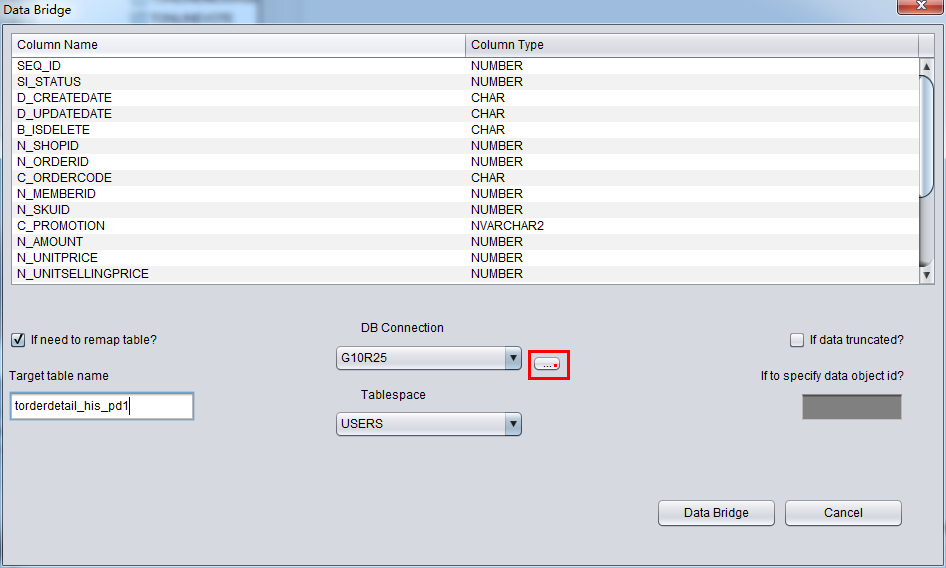
Attention on DataBridge recovering truncated/dropped table: when you recovering truncated/dropped and insert data back to source DB, users should choose another tablespace which diffs from the original tablespace. If export data into same tablespace, oracle will reuse space which stores truncated/dropped table, and can make data overwritten, we will lose the last resort to recover the data.
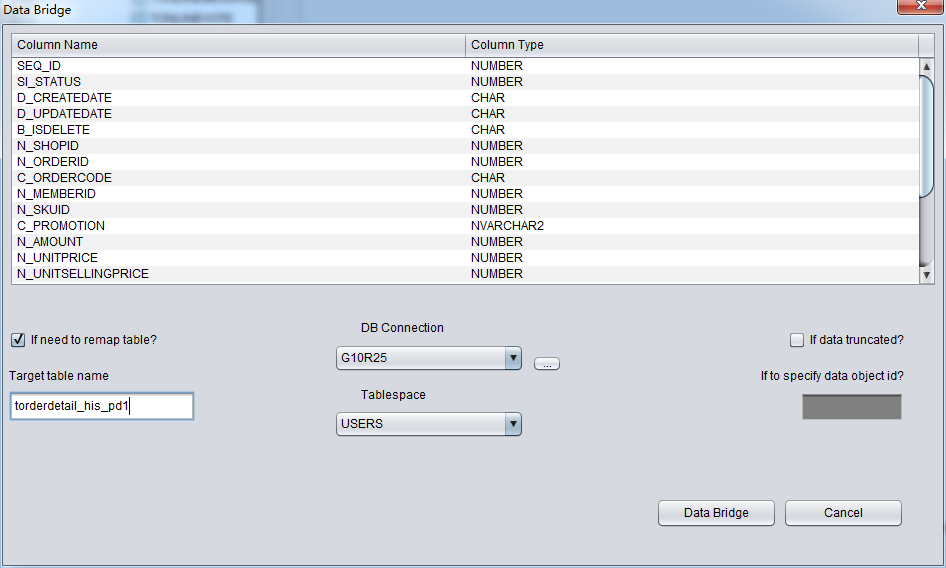
For example, we truncated a table and would like to user DataBridge to recover data back to source database, but we would like to use another table name. Original table name is torderdetail_his, and user can select “if need to remap table” and input proper destination name, as below:
Attention: 1) For destination DB which already had the same table name, PRM-DUL will not recreate a table but append all recovered data. 2) For destination DB which did not have source table name, PRM-DUL would try to create table and recover the data.
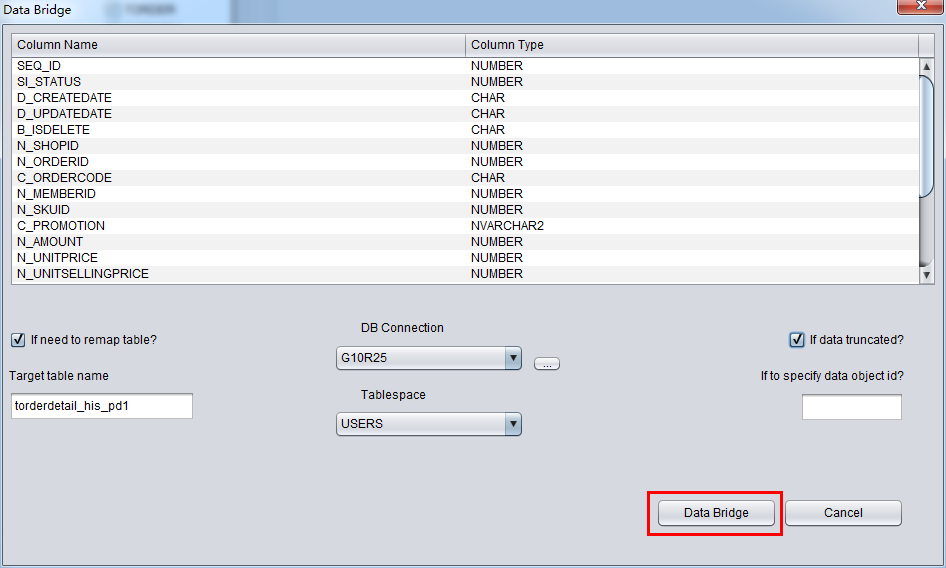
In this case, we would recover Truncated data, therefore, please select “if data truncated?” checkbox, Or, PRM-DUL would do regular data extraction, but not Truncated data.
Truncate recovery methodology is: Oracle will only update table DATA_OBJECT_ID in data dictionary and segment header. Therefore, the real data will not be overwritten. Due to the difference between dictionary and DATA_OBJECT_ID, Oracle server process will not read truncated data while scanning table. But, the real data is still there.
PRM-DUL will try to scan 10M-bytes blocks which are behind of the table’s segment header, if some blocks with smaller DATA_OBJECT_ID than the object’s current DATA_OBJECT_ID, then PRM-DUL thinks it find something useful.
There is a blank input field called ”if to specify data object id”, which let user input Data Object ID. Usually, you don’t need to input any value, unless the recovery does not work. We suggest user to contact ParnassusData for help.
Click DataBridge button ,then it will start extracting if the configuration is done.
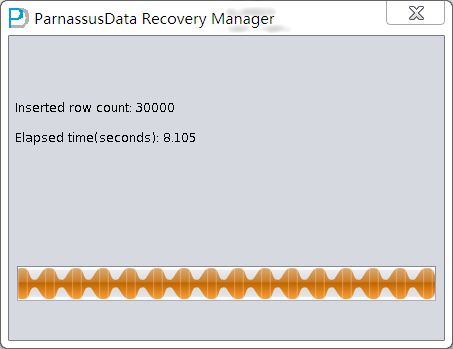
DataBridge will display the successfully rescued rows and elapsed time.
Case 3: Oracle Dictionary Corrupted, DB can not be open
DBA of company D deleted SYS.TS$ (A bootstrap Table) by mistake, this cause Oracle DB can not be open
| Oracle Database 11g Enterprise Edition Release 11.2.0.3.0 – 64bit ProductionWith the Partitioning, Automatic Storage Management, OLAP, Data Miningand Real Application Testing options
INSTANCE_NAME —————- ASMME
SQL> SQL> SQL> select count(*) from sys.ts$;
COUNT(*) ———- 5
SQL> delete ts$;
5 rows deleted.
SQL> commit;
Commit complete.
SQL> shutdown immediate; Database closed. Database dismounted. ORACLE instance shut down.
Database mounted. ORA-01092: ORACLE instance terminated. Disconnection forced ORA-01405: fetched column value is NULL Process ID: 5270 Session ID: 10 Serial number: 3
Undo initialization errored: err:1405 serial:0 start:3126020954 end:3126020954 diff:0 (0 seconds) Errors in file /s01/diag/rdbms/asmme/ASMME/trace/ASMME_ora_5270.trc: ORA-01405: fetched column value is NULL Errors in file /s01/diag/rdbms/asmme/ASMME/trace/ASMME_ora_5270.trc: ORA-01405: fetched column value is NULL Error 1405 happened during db open, shutting down database USER (ospid: 5270): terminating the instance due to error 1405 Instance terminated by USER, pid = 5270 ORA-1092 signalled during: ALTER DATABASE OPEN… opiodr aborting process unknown ospid (5270) as a result of ORA-1092
|
In this circumstance, data dictionary had been damaged; therefore it would be very hard to open the database.
Then, we can use PRM-DUL rescue data in DB. Following processes as below:
- Recovery Wizard
- Select Data Dictionary Mode
- Choose Big or Little Endian , and input DB NAME
- Click Load for database loading
- Extract Tables
Case 4: Deleted SYSTEM tablespace by mistake
A System Administrator of company D who deleted SYSTEM tablespace by mistake and make DB can not be open. Unfortunately, there is no RMAN backup available. Therefore, for company D try to use PRM-DUL to recover all data.
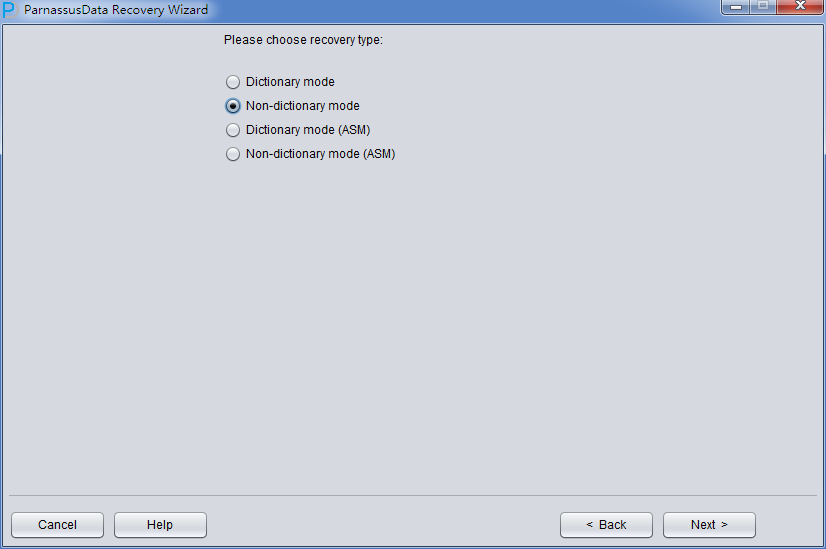
In this circumstance, run PRM-DUL and go into Recovery Wizard. Select “Non-Dictionary mode”:
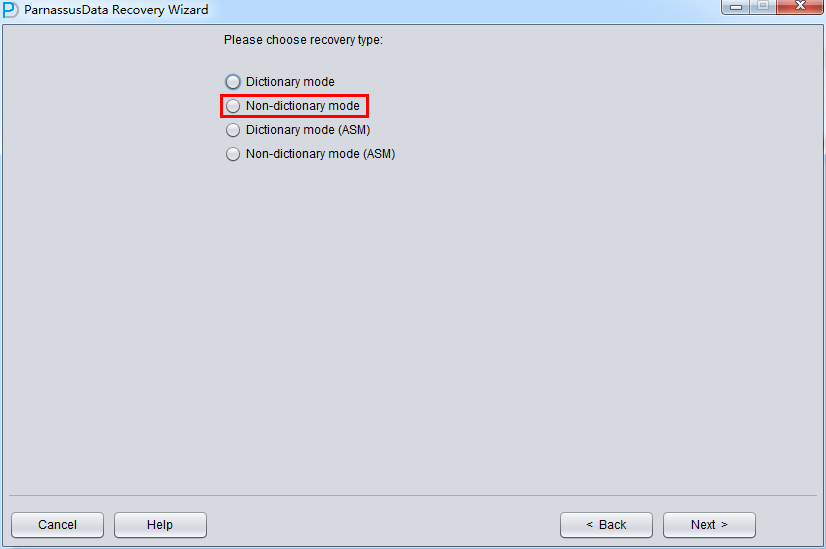
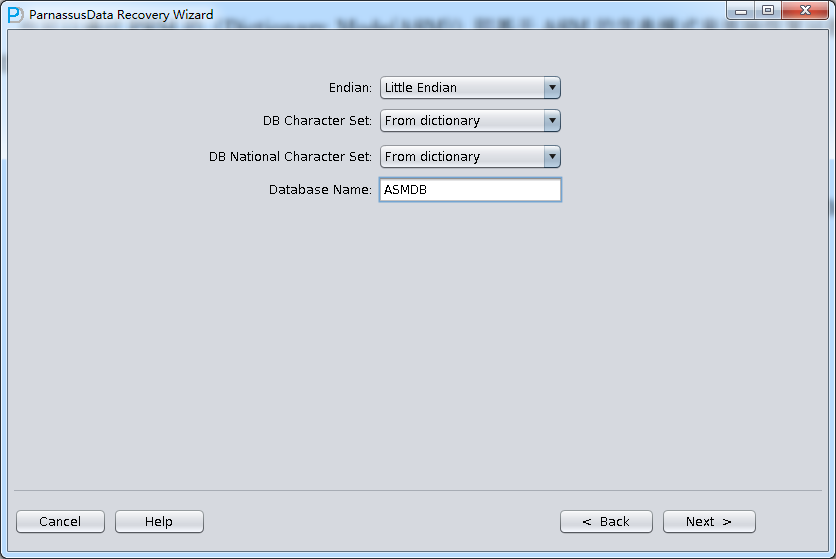
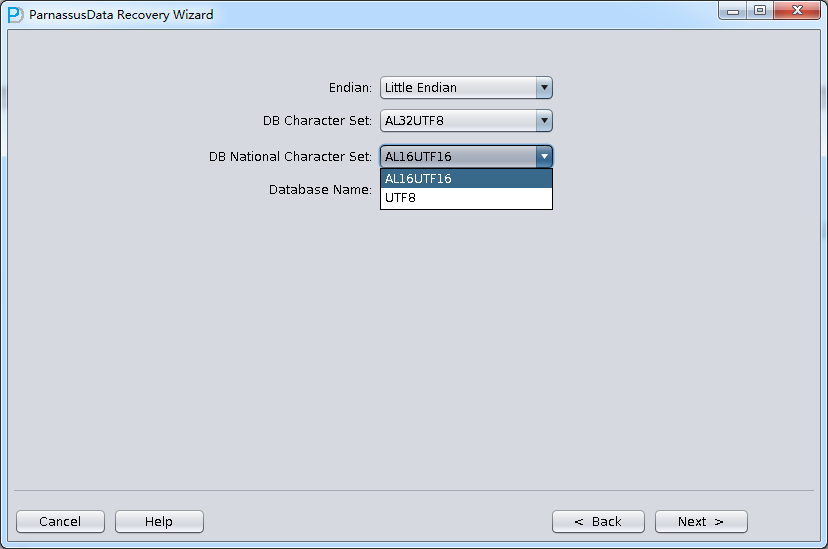
In No-dictionary mode, we have to select DB Character Set and DB National Character Set. Because of while losing SYSTEM tablespace, database cannot find character set information.
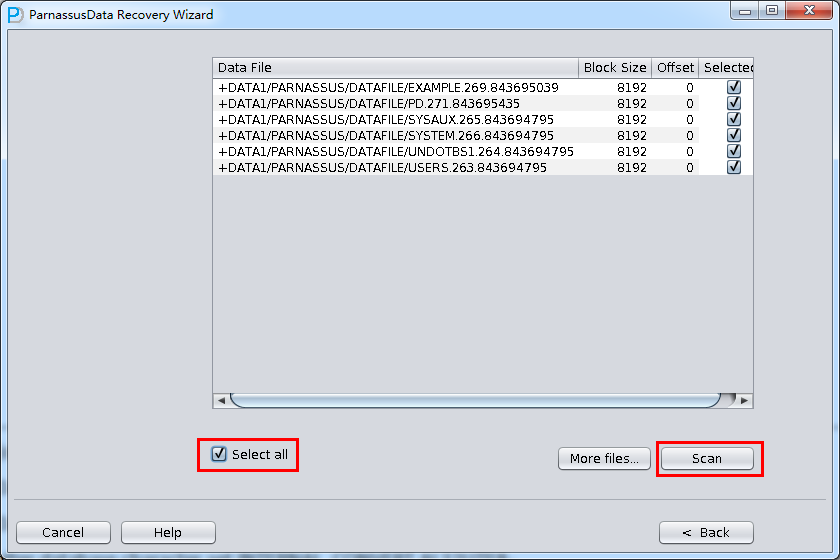
Similarly as case 1, select all data (not including temp file), and correct Block Size and OFFSET
Then click scan button. Then PRM-DUL will scan all segment header and extents in datafile, and record it into SEG$.DAT and EXT$.DAT. In Oracle, each partition table or non-partition table has a segment header. Once we find segment header, we could find the whole table extent map information. Via extent map, we can get all record.
There is one exception, for example, there is one non-partition table that is stored in two database files. The segment header and half data are stored in datafile A, and the others are on datafile B. While system tablespace and datafile A are lost, PRM-DUL couldn’t find segment header associated with problem table, but it can scan datafile B and get the rest extent map.
In order to recover data via segment header and extent map in no-dictionary mode.
PRM-DUL will create two files: SEG$.DAT(stores segment header info) and EXT$.DAT(stores extent info) ,which is also recorded in PRM-DUL embedded database.
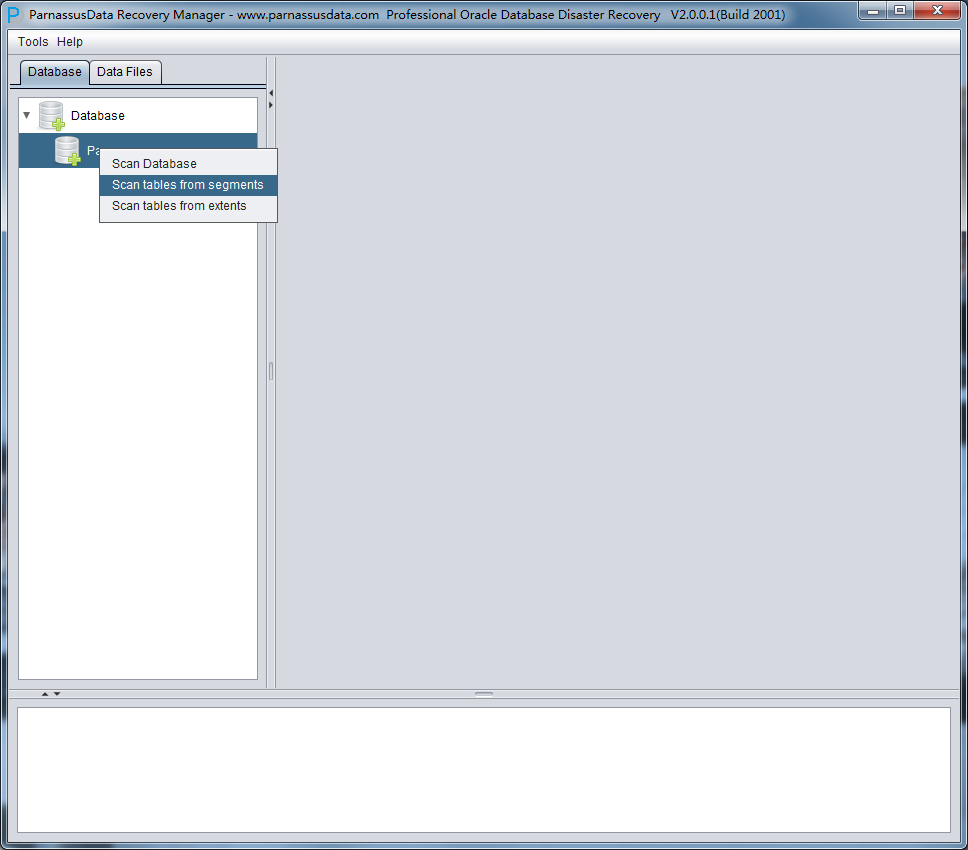
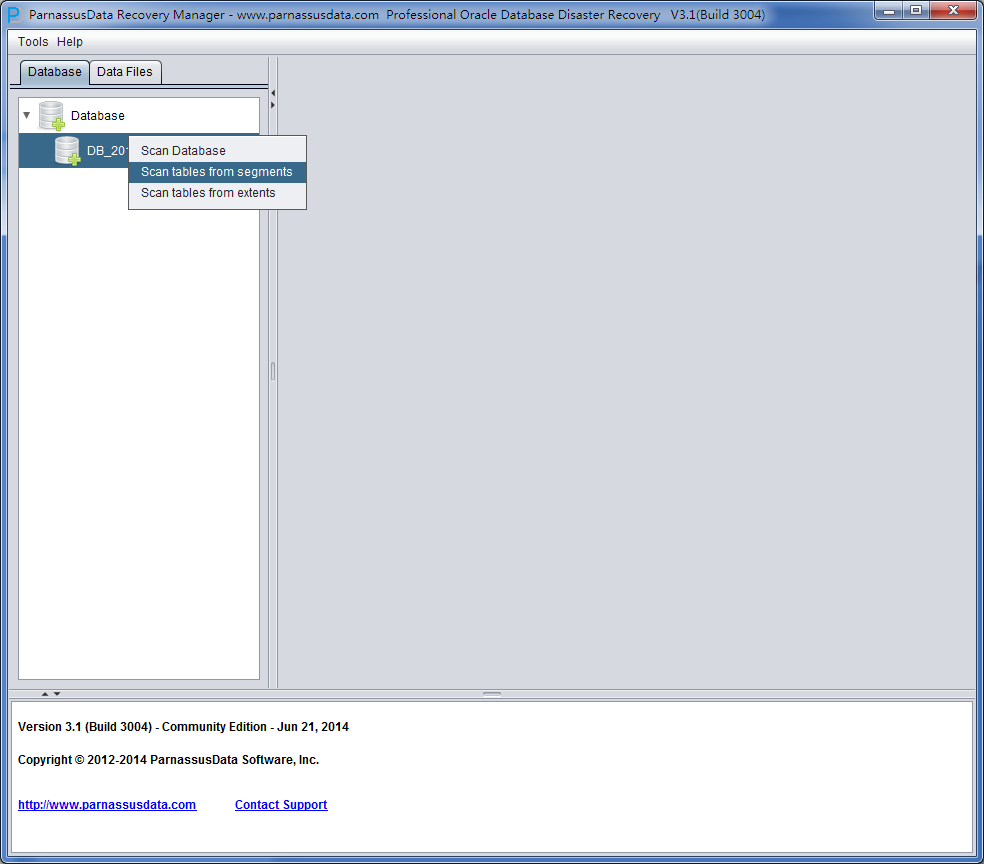
After scan, there is database icon on the left.
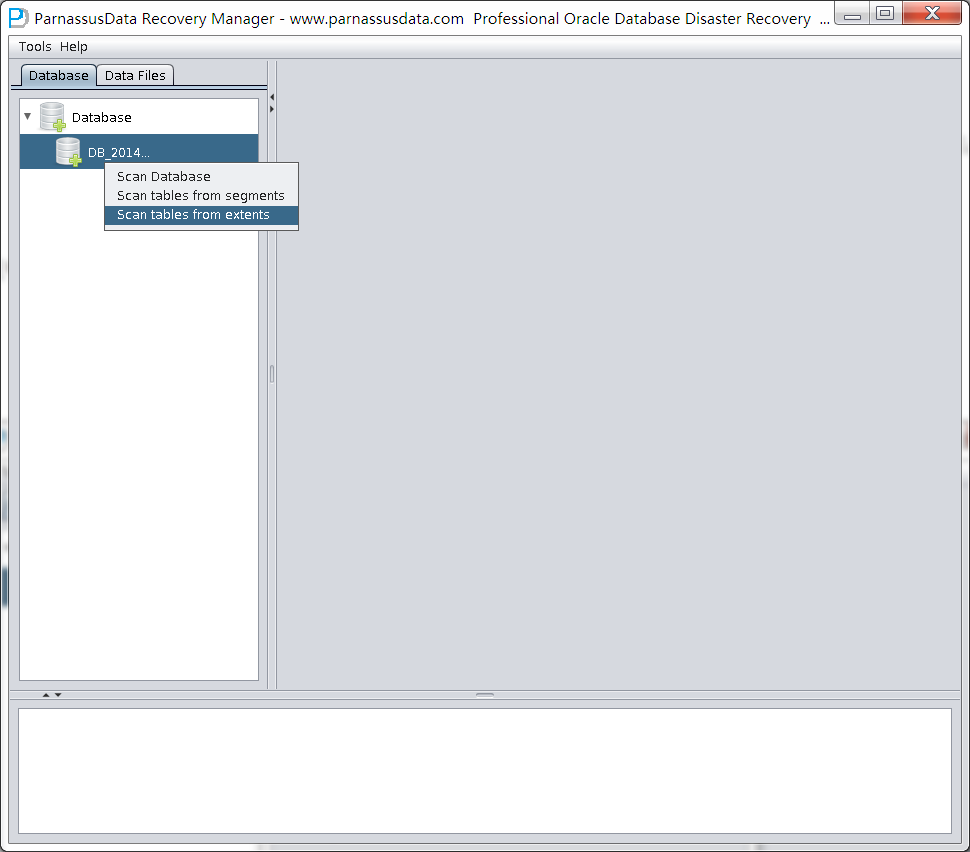
Meanwhile, there are 2 option:
- Scan Tables From Segments:
- System tablespace lost, but user tablespace datafiles are there
- Scan Tables From Extents
- Only used when truncated data can not be recovered by Dictionary-Mode
- Both system tablespace and segment header are lost
It is not necessary to use mode “Scan Tables From Extents” at the first time, unless you can’t find your data by “Scan Tables From Segment”.
Scan tables From segments should be your first choice.
After scanning tables from segments, there will be a tree diagram on the left.
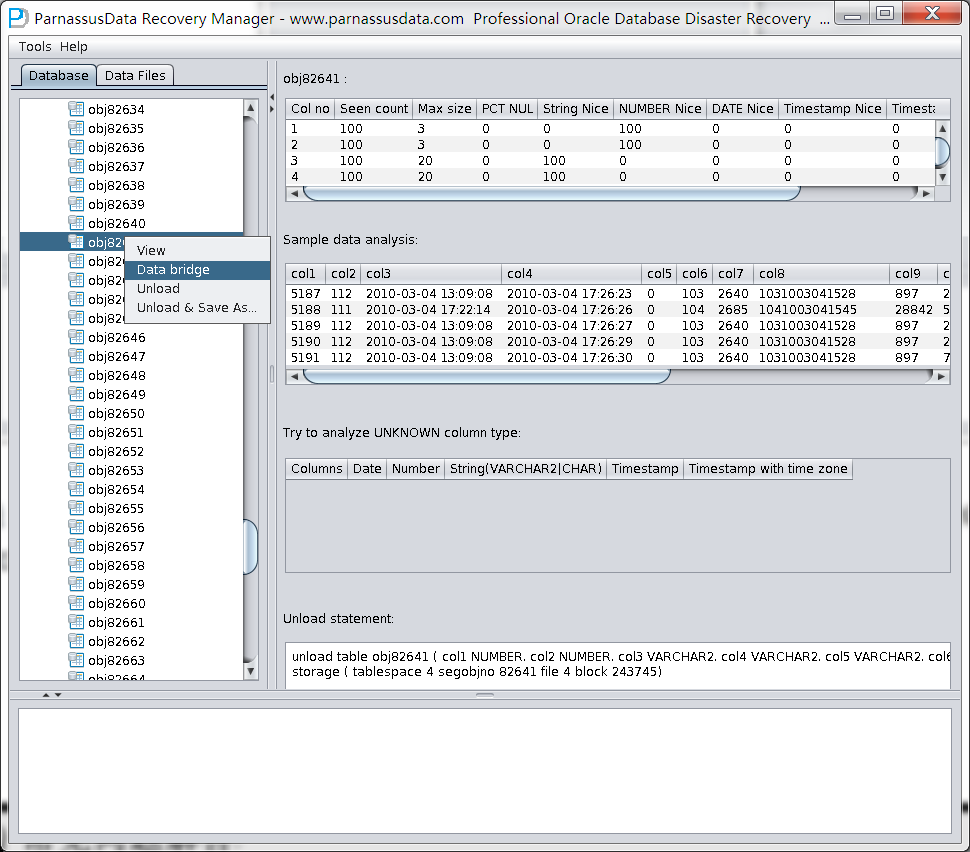
Scan Tables is for constructing the data based on segment header in SEG$. The name of each node in the diagram is named by obj+ DATA OBJECT ID.
Click on node and check right side:
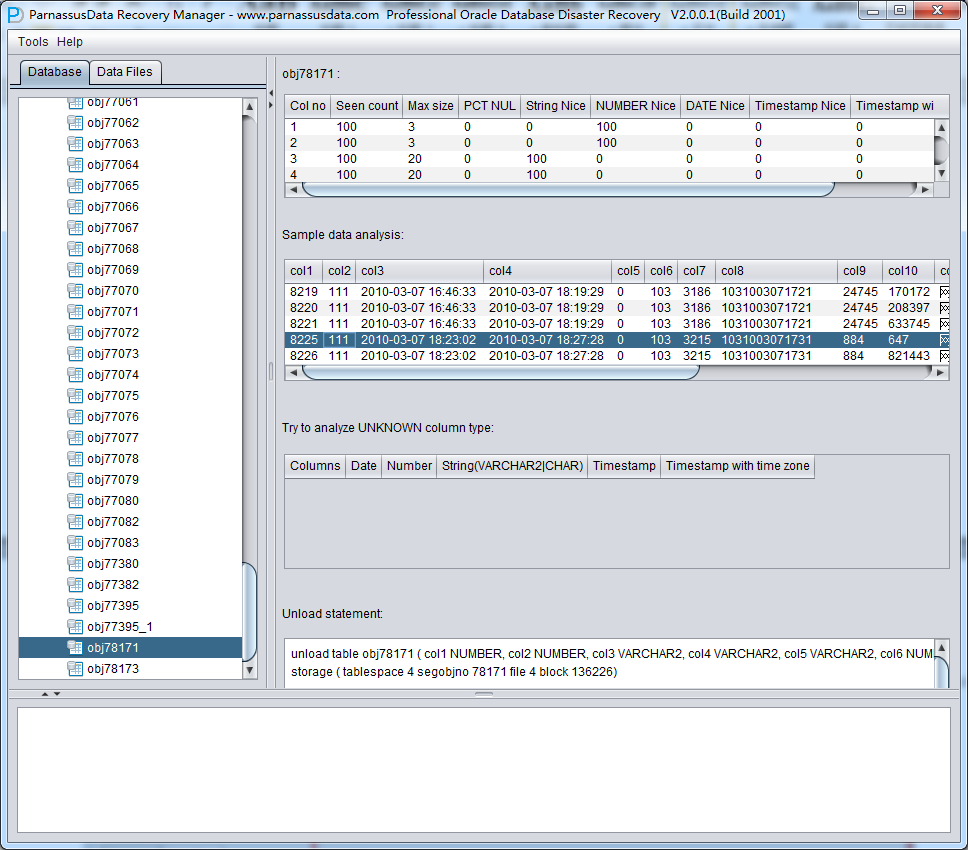
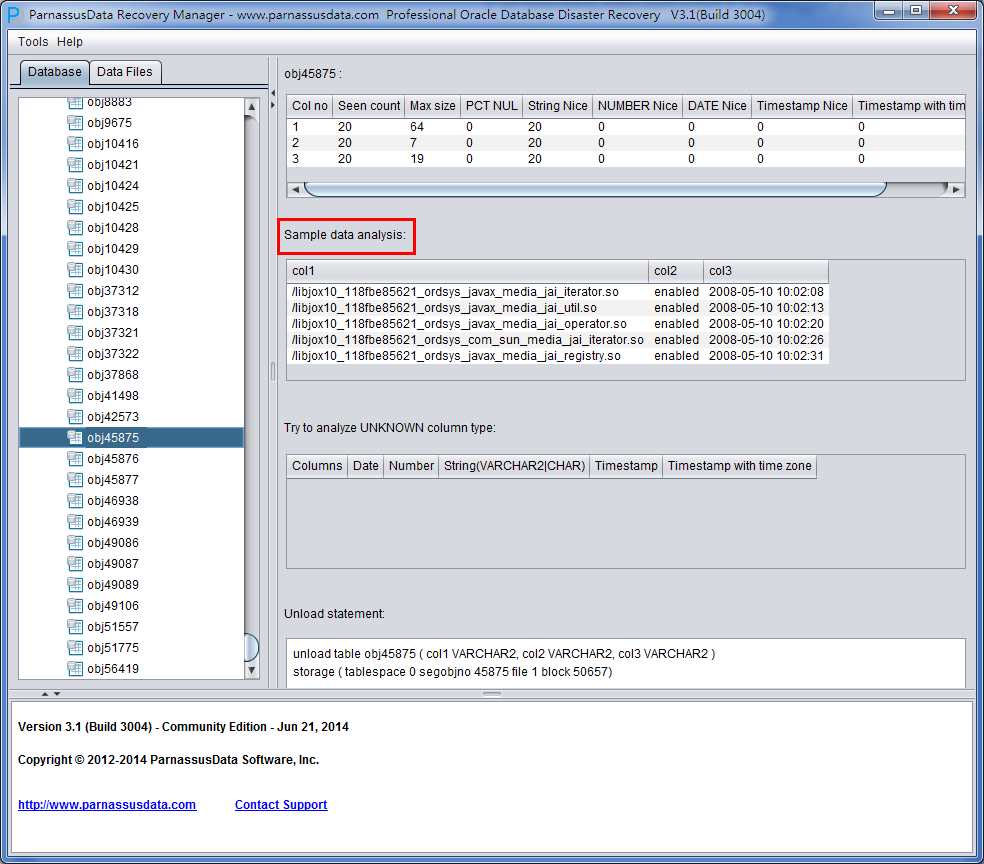
Intelligence on Data Analysis
Because of SYSTEM tablespace lost, there is not data structure information available in NO-Dictionary mode. The column information includes column name and data type. All these are storage in dictionary but not in table. Therefore, PRM-DUL need to guess the data type. PRM-DUL has a JAVA pre analysis algorithm, and has the ability to analysis more than 10 kinds of types.、
Intelligence analysis can successfully guess 90% of columns in most of circumstances
On the right side, the meaning of columns:
- Col1 no
- Seen Count
- MAX SIZE
- PCT NULL
- String Nice
- Number Nice
- Date Nice
- Timestamp Nice
- Timestamp with timezone Nice
Sample Data Analysis:
Intelligence Analysis will analyze 10 records and display the results. These results will help client to know the column information.
As in the picture, the there are 10 records which had been displayed all.
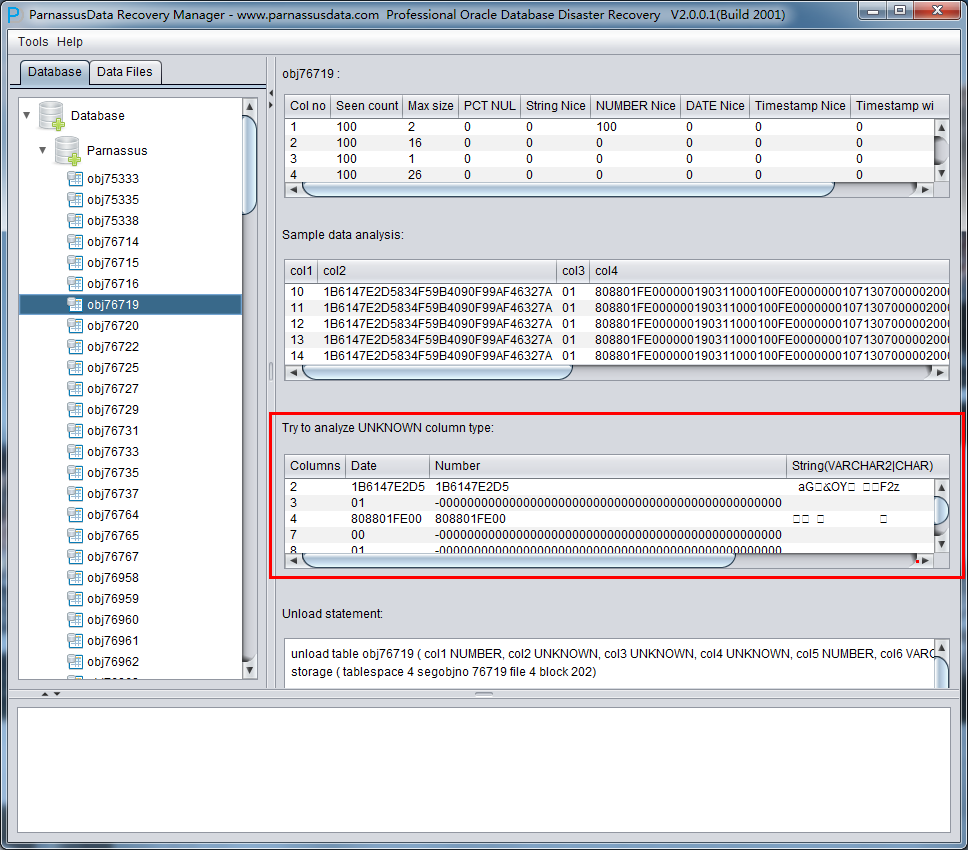
TRY TO ANALYZE UNKNOWN column type:
If PRM-DUL cannot recognize the column’s data type , you can specify data type by yourself.
So far, PRM-DUL does not support below types:
XDB.XDB$RAW_LIST_T、XMLTYPE、Customized TYPE
Unload Statement:
PRM-DUL generated unload scripts, and these scripts can be only used by PRM-DUL support engineers.
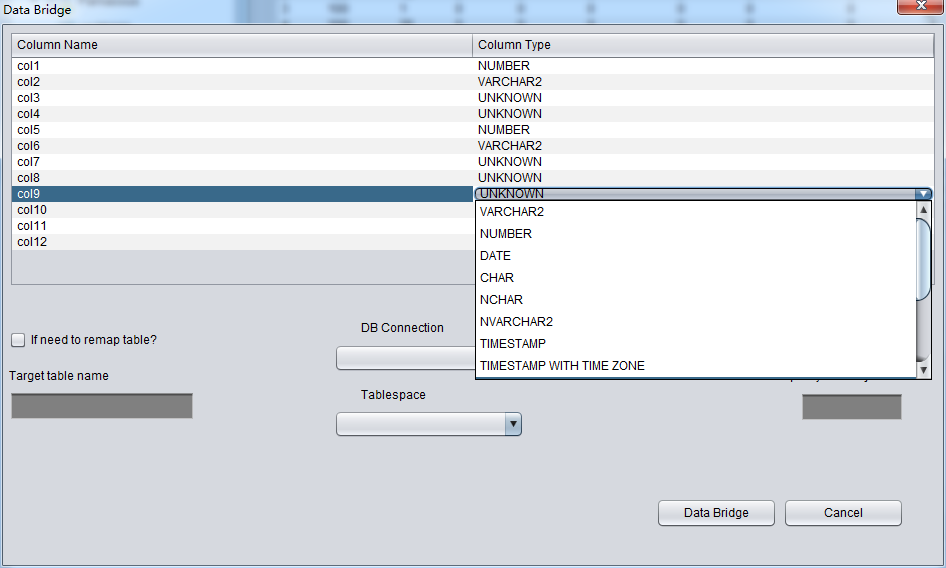
In “Non-Dictionary Mode”, Data Bridge is also applicable. Comparing ” Dictionary Mode”, the manger difference that the user can define the type in data transferring. As below picture, the column type is UNKNOW. These types might be PRM-DUL unsupported types for example: XML and etc.
If the user know the data type in this table (from schema design documents), it is necessary to specify the correct types manually.
CASE 5:deleted System Tablespace and Part of User tablespace datafile by mistake
User D deleted the system tablespace and part of user tablespace datafile by mistake.
In this circumstance, part of user data table was deleted, and this might includes datafile which stored segment header. Therefore it is better to use “Scan Tables From Extents” than” Scan Tables From Segment Header”.
Steps as Below:
- Go to Recovery Wizard, select No-Dictionary mode,and added all usable data file. Then process them to scan database.
- Select database, and right click Scan Tables From Extents
- Analyze the data and implement data extraction and Data Bright
- Following steps are the same with Case 4
CASE 6: rescue datafile from damaged diskgroup which can’t be mounted
User D chooses ASM instead of other filesystem. Since there are many bugs in version 11.2.0.1, it may happen that ASM DISKGROUP cannot be mounted or it does not work after repairing ASM Disk Header.
In this circumstance, user can use ASM Files Clone feature of PRM-DUL to rescue datafile from damaged ASM DiskGroup directly.
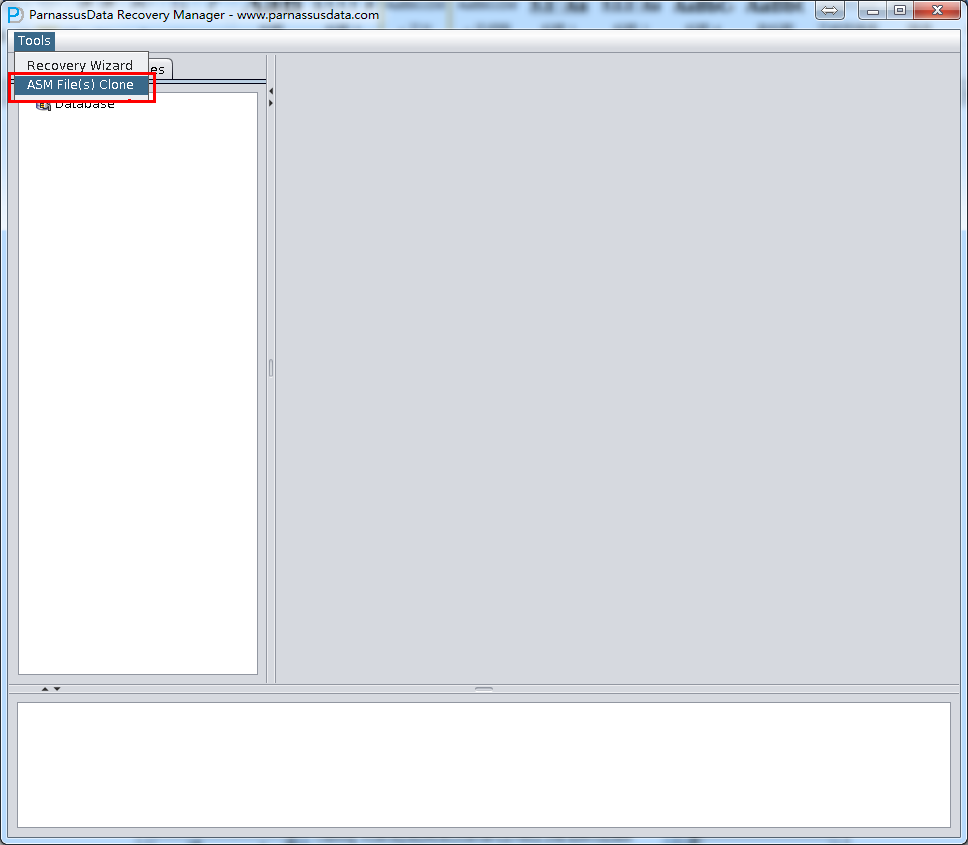
- Open main interface, and select ASM File(s) Clone:
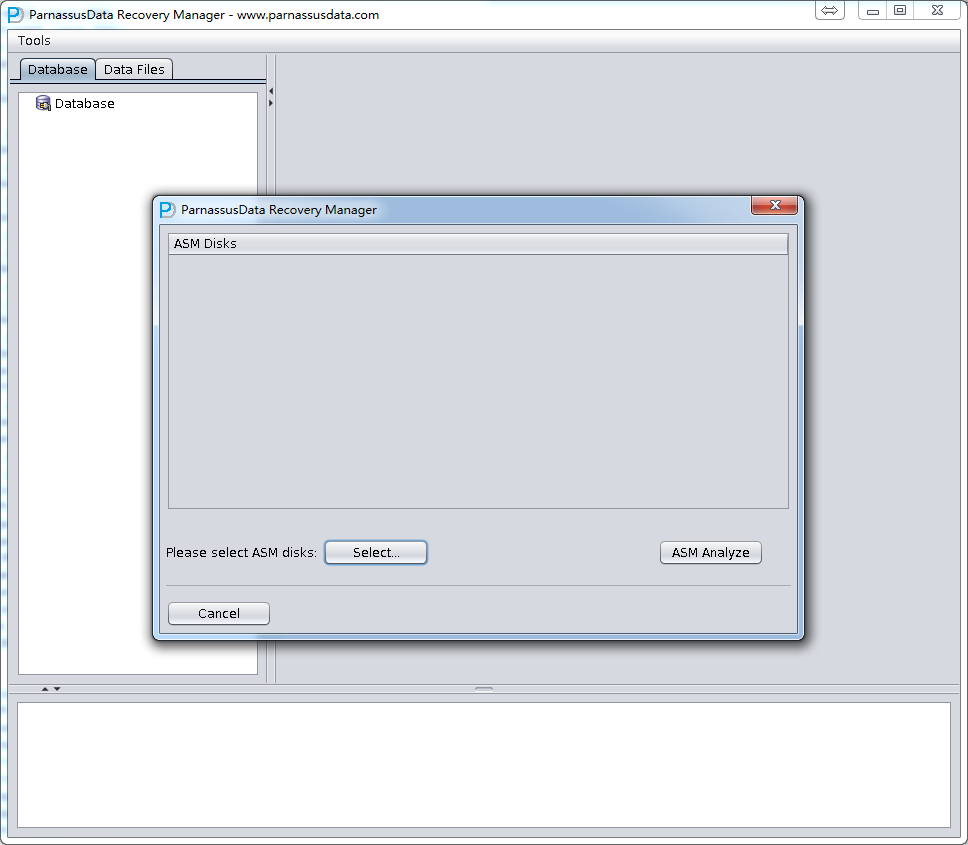
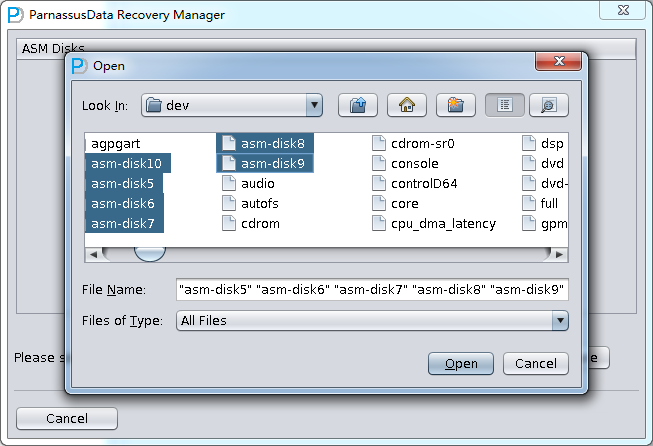
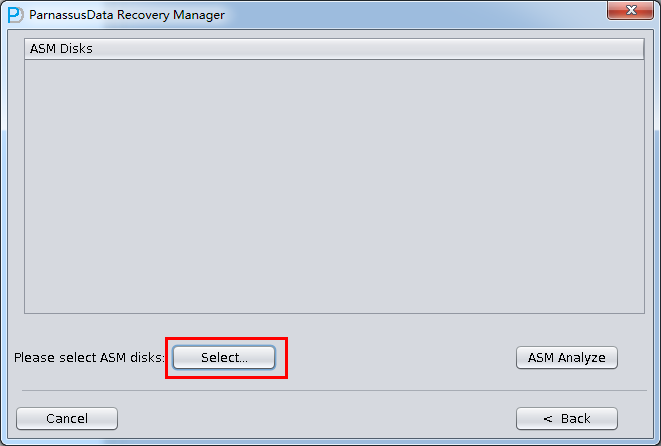
- Enter ASM Disks Window, and click SELECt…to add ASM Disks. For example: /dev/asm-disk5(linux). And click ASM analyze.
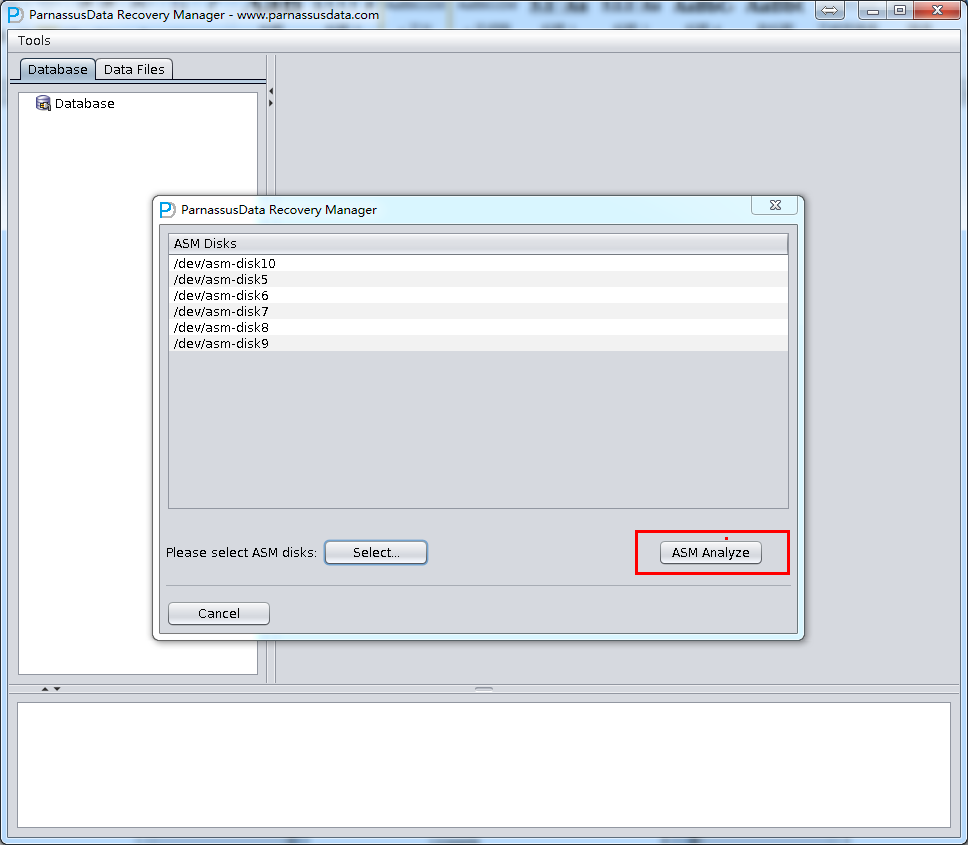
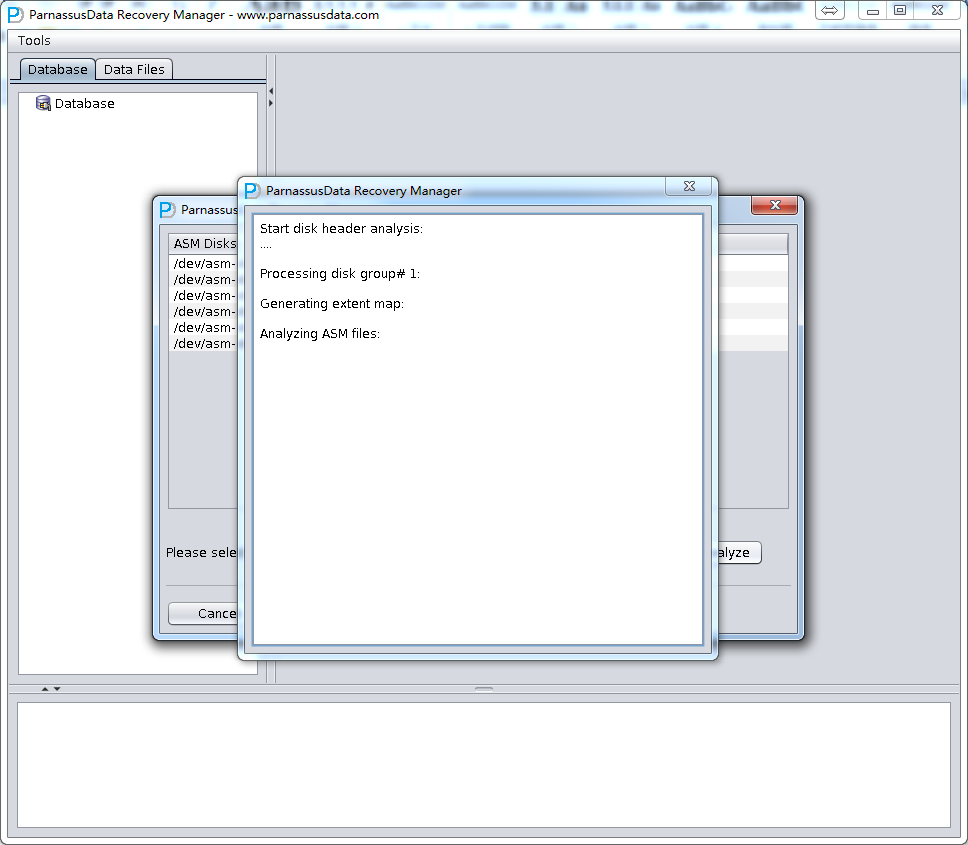
ASM Files Clone feature will analyze ASM Disk header, in order to finding Disk group file and File Extent Map. All the information is recorded into PRM-DUL embedded database. PRM-DUL can collect all Metadata, and analyze to show diagram.
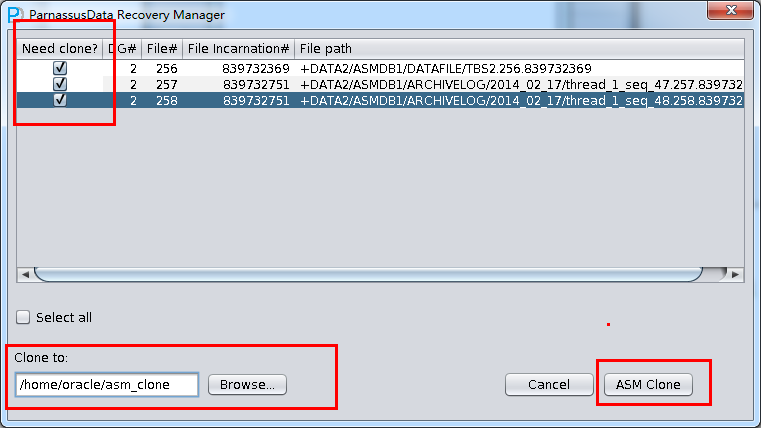
- After analysis of ASM Analyze, PRM-DUL will find the file list in Disk groups. Users can select the datafile/archivelog which need to be cloned to destination folder.
Click ASM Clone to start…
There is progress bar while file cloning.
ASM File Clone log as below:
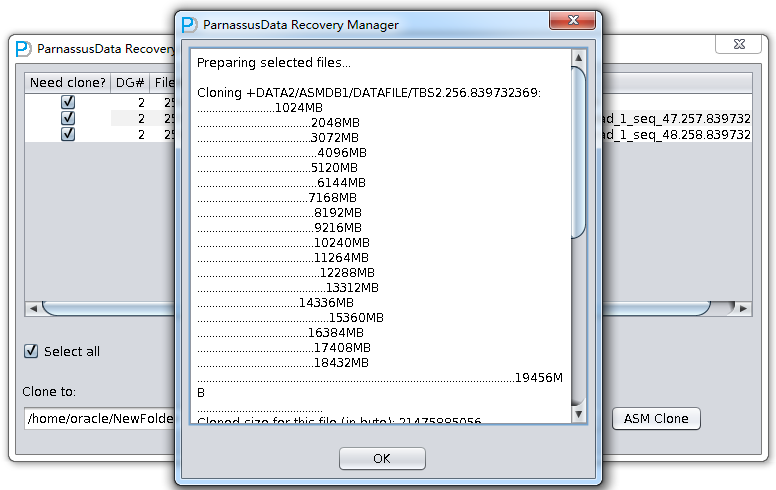
| Preparing selected files…Cloning +DATA2/ASMDB1/DATAFILE/TBS2.256.839732369:……………………..1024MB………………………………..2048MB
………………………………..3072MB ………………………………….4096MB ………………………………..5120MB ………………………………….6144MB ……………………………….7168MB …………………………………8192MB …………………………………9216MB …………………………………10240MB …………………………………11264MB …………………………………..12288MB …………………………………….13312MB …………………………….14336MB ……………………………………..15360MB ……………………………….16384MB …………………………………17408MB …………………………………18432MB …………………………………………………………………………………………….19456MB …………………………………… Cloned size for this file (in byte): 21475885056
Cloned successfully!
Cloning +DATA2/ASMDB1/ARCHIVELOG/2014_02_17/thread_1_seq_47.257.839732751: …… Cloned size for this file (in byte): 29360128
Cloned successfully!
Cloning +DATA2/ASMDB1/ARCHIVELOG/2014_02_17/thread_1_seq_48.258.839732751: …… Cloned size for this file (in byte): 1048576
Cloned successfully!
All selected files were cloned done. |
- It is necessary to validate cloned data via “dbv” or “rman validate”, for example:
| rman target /RMAN> catalog datafilecopy ‘/home/oracle/asm_clone/TBS2.256.839732369.dbf’;
cataloged datafile copy datafile copy file name=/home/oracle/asm_clone/TBS2.256.839732369.dbf RECID=2 STAMP=839750901
RMAN> validate datafilecopy ‘/home/oracle/asm_clone/TBS2.256.839732369.dbf’;
Starting validate at 17-FEB-14 using channel ORA_DISK_1 channel ORA_DISK_1: starting validation of datafile channel ORA_DISK_1: including datafile copy of datafile 00016 in backup set input file name=/home/oracle/asm_clone/TBS2.256.839732369.dbf channel ORA_DISK_1: validation complete, elapsed time: 00:03:35 List of Datafile Copies ======================= File Status Marked Corrupt Empty Blocks Blocks Examined High SCN —- —— ————– ———— ————— ———- 16 OK 0 2621313 2621440 1945051 File Name: /home/oracle/asm_clone/TBS2.256.839732369.dbf Block Type Blocks Failing Blocks Processed ———- ————– —————- Data 0 0 Index 0 0 Other 0 127
Finished validate at 17-FEB-14
|
When using PRM-DUL in ASM of ASMLIB?
Simple and Clear: asmlib related ASM DISK is stored in OS as ll /dev/oracleasm/disks. For example: Add files of /dev/oracleasm/disks into PRM-DUL ASM DISK
| $ll /dev/oracleasm/diskstotal 0brw-rw—- 1 oracle dba 8, 97 Apr 28 15:20 VOL001brw-rw—- 1 oracle dba 8, 81 Apr 28 15:20 VOL002brw-rw—- 1 oracle dba 8, 65 Apr 28 15:20 VOL003
brw-rw—- 1 oracle dba 8, 49 Apr 28 15:20 VOL004 brw-rw—- 1 oracle dba 8, 33 Apr 28 15:20 VOL005 brw-rw—- 1 oracle dba 8, 17 Apr 28 15:20 VOL006 brw-rw—- 1 oracle dba 8, 129 Apr 28 15:20 VOL007 brw-rw—- 1 oracle dba 8, 113 Apr 28 15:20 VOL008 |
CASE 7: DB(stored in ASM) can not be opened
One of CRM database in company D can’t be opened due to adding disk which has I/O error into ASM diskgroup. This operation generated some corrupted block in datafile of system tablespace, and user failed to open DB any more.
In the circumstance, we can use PRM-DUL ASM Diskgroup to clone all datafile out of ASM.
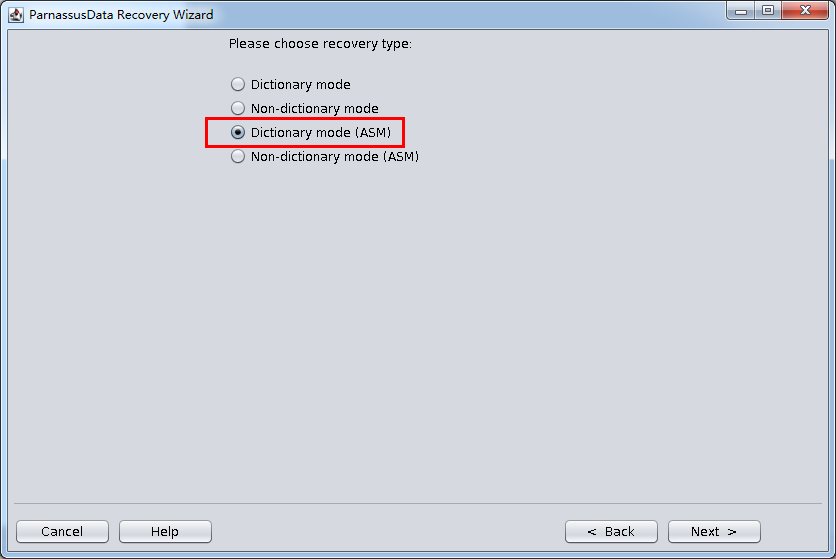
Or, user can also use “Dictionary Mode(ASM)” to recover data from this ASM environment . Steps as below:
- Recovery Wizard
- Dictionary Mode(ASM)
- Add ASM DISK (all ASM DISK in your recovery disks)
- Click ASM analyze
- Select suitable Endian
- In ASM analyze, it lists all database file, or click “select all”
Click “load”, following steps are the same with case3
CASE 8: Recover Lost system tablespace in ASM
User D deleted system tablespace FILE#=1 datafile and user tablespace. This make alter database open failed.
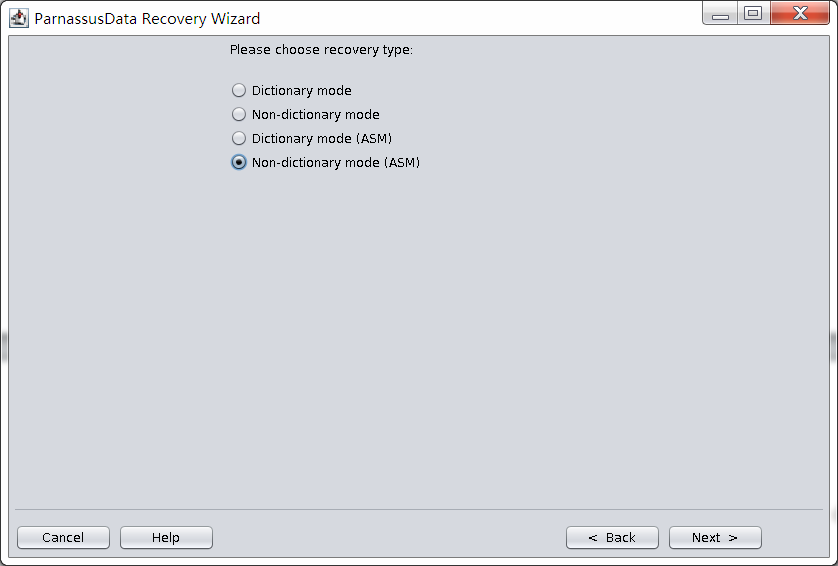
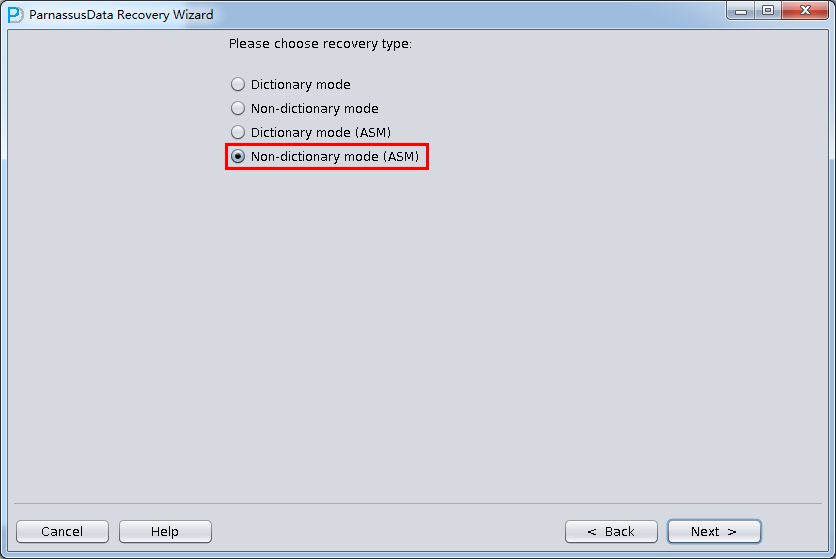
In this circumstance, user can use” Non-Dictionary Mode (ASM)” to recover data.
Steps as below:
- Recovery Wizard
- Non-Dictionary Mode (ASM)
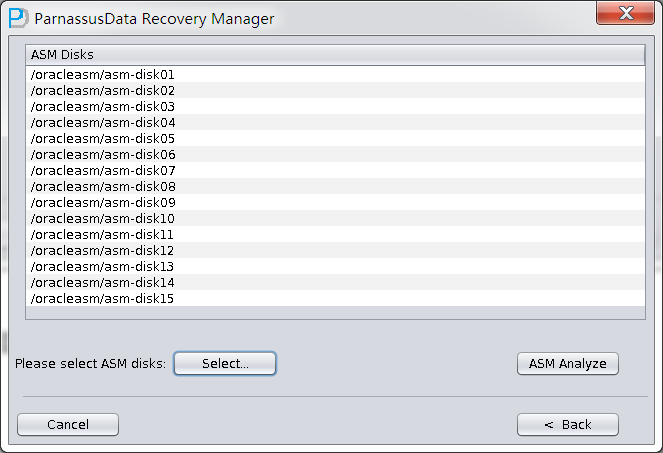
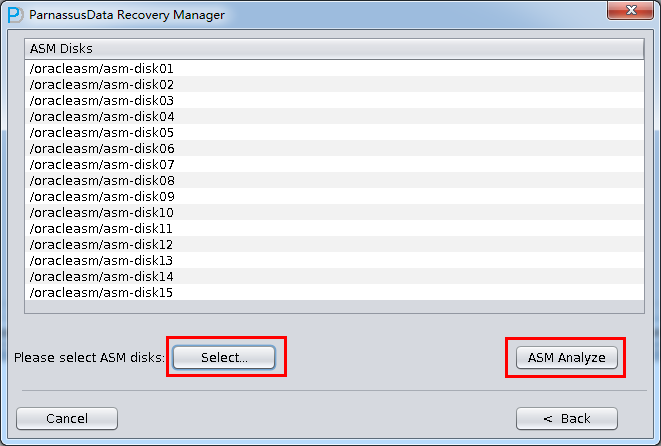
- Add necessary ASM Disk
- Click ASM analyze
- Select the suitable Endian and Character set. (Manually select character set due to Non-Dictionary Mode)
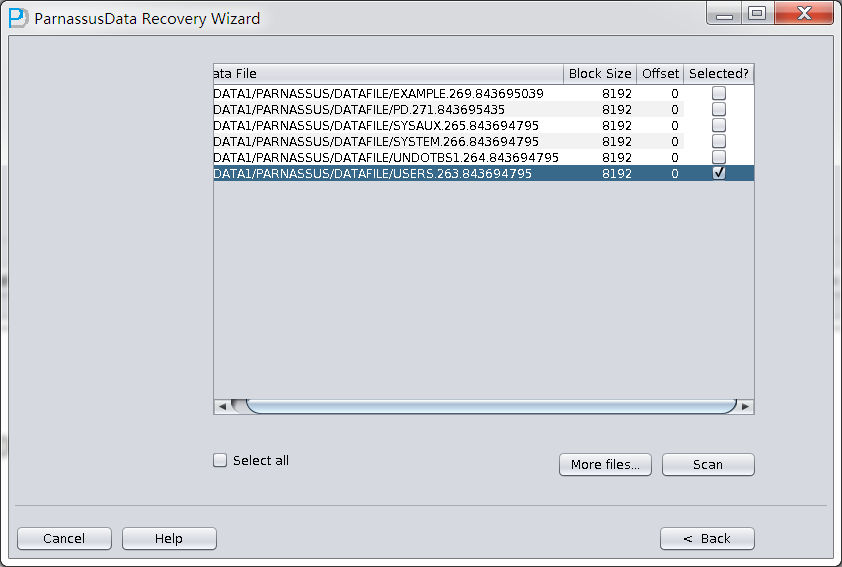
- Select all data file, or click “Select all”
- Click “scan”, following steps are the same with Case 3
CASE 9: Recover DROP TABLESPACE Data
User D dropped a tablespace(“DROP TABLESAPCE INCLUDING CONTENTS”) by mistake. They want to recover data resided in that tablespace, but there is no RMAN backup.
Therefore, we can use PRM-DUL No-Dictionary mode to recover data. In this way, we can extract most data. However, the data is not mapping to the dictionary. Users need to manually recognize the table. Since it changed data dictionary by DROPPING TABLE and deleted objects in OBJ$, we can not have the relationship between DATA_OBJECT_ID and OBJECT_NAME. Below is the instruction of getting mapping.
| select tablespace_name,segment_type,count(*) from dba_segments where owner=’PARNASSUSDATA’ group by tablespace_name,segment_type;TABLESPACE SEGMENT_TYPE COUNT(*)———- ————— ———-
USERS TABLE 126 USERS INDEX 136
SQL> select count(*) from obj$;
COUNT(*) ———- 75698
SQL> select current_scn, systimestamp from v$database;
CURRENT_SCN ———– SYSTIMESTAMP ————————————————————————— 1895940 25-4月 -14 09.18.00.628000 下午 +08:00
SQL> select file_name from dba_data_files where tablespace_name=’USERS’;
FILE_NAME ——————————————————————————– H:\PP\MACLEAN\ORADATA\PARNASSUS\DATAFILE\O1_MF_USERS_9MNBMJYJ_.DBF
SQL> drop tablespace users including contents;
C:\Users\maclean>dir H:\APP\MACLEAN\ORADATA\PARNASSUS\DATAFILE\O1_MF_USERS_9MNBMJYJ_.DBF
The volume is entertainment in drive H and SN is A87E-B792
H:\APP\MACLEAN\ORADATA\PARNASSUS\DATAFILE
The drive can not find the file
|
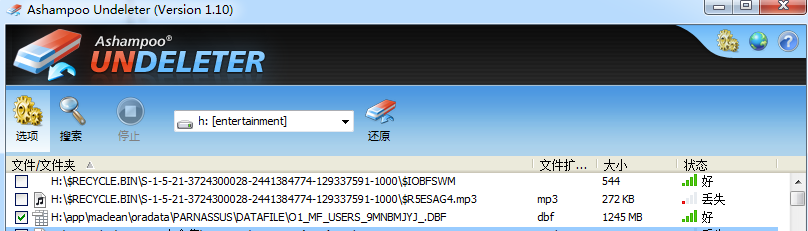
Here, we can use other file recovery tool for data file recovery, for example: Undeleter on Windows.
Startup PRM-DUL => recovery Wizard => No-Dictionary
This is No-Dictionary mode, and please select correct character set
Add the files recovered and click scan
Start from the head segments, if it can not find all table, try to use extend scan:
You can find lots of node named OBJXXXXX,this name is combination of “OBJ” and DATA_OBJECT_ID. We need some guy who is familiar with schema design and application data, he can clarify the relationship between data and table.
If there is no body can clarify the relationship between data and table, try below methods:
In this case, only user tablespace had been dropped and Oracle still works, and to get the mapping of DATA_OBJECT_ID and table name by FLASHBACK QUERY.
| SQL> select count(*) from sys.obj$;COUNT(*)———-75436
SQL> select count(*) from sys.obj$ as of scn 1895940; select count(*) from sys.obj$ as of scn 1895940 * Error: ORA-01555: Snapshot is too old,
Try to use DBA_HIST_SQL_PLAN of AWR and find the mapping between OBJECT# and OBJECT_NAME in recent 7 days.
SQL> desc DBA_HIST_SQL_PLAN NAME NULL? TYPE —————————————– ——– ———————– DBID NOT NULL NUMBER SQL_ID NOT NULL VARCHAR2(13) PLAN_HASH_VALUE NOT NULL NUMBER ID NOT NULL NUMBER OPERATION VARCHAR2(30) OPTIONS VARCHAR2(30) OBJECT_NODE VARCHAR2(128) OBJECT# NUMBER OBJECT_OWNER VARCHAR2(30) OBJECT_NAME VARCHAR2(31) OBJECT_ALIAS VARCHAR2(65) OBJECT_TYPE VARCHAR2(20) OPTIMIZER VARCHAR2(20) PARENT_ID NUMBER DEPTH NUMBER POSITION NUMBER SEARCH_COLUMNS NUMBER COST NUMBER CARDINALITY NUMBER BYTES NUMBER OTHER_TAG VARCHAR2(35) PARTITION_START VARCHAR2(64) PARTITION_STOP VARCHAR2(64) PARTITION_ID NUMBER OTHER VARCHAR2(4000) DISTRIBUTION VARCHAR2(20) CPU_COST NUMBER IO_COST NUMBER TEMP_SPACE NUMBER ACCESS_PREDICATES VARCHAR2(4000) FILTER_PREDICATES VARCHAR2(4000) PROJECTION VARCHAR2(4000) TIME NUMBER QBLOCK_NAME VARCHAR2(31) REMARKS VARCHAR2(4000) TIMESTAMP DATE OTHER_XML CLOB
For exmaple:
select object_owner,object_name,object# from DBA_HIST_SQL_PLAN where sql_id=’avwjc02vb10j4′
OBJECT_OWNER OBJECT_NAME OBJECT# ——————– —————————————- ———-
PARNASSUSDATA TORDERDETAIL_HIS 78688
Use below scrip for the mapping relationship between OBJECT_ID and OBJECT_NAME
Select * from (select object_name,object# from DBA_HIST_SQL_PLAN UNION select object_name,object# from GV$SQL_PLAN) V1 where V1.OBJECT# IS NOT NULL minus select name,obj# from sys.obj$;
select obj#,dataobj#, object_name from WRH$_SEG_STAT_OBJ where object_name not in (select name from sys.obJ$) order by object_name desc;
another script: SELECT tab1.SQL_ID, current_obj#, tab2.sql_text FROM DBA_HIST_ACTIVE_SESS_HISTORY tab1, dba_hist_sqltext tab2 WHERE tab1.current_obj# NOT IN (SELECT obj# FROM sys.obj$ ) AND current_obj#!=-1 AND tab1.sql_id =tab2.sql_id(+);
|
Attention: Since it relies on AWR repository, the mapping table is not that accurate and exact.
CASE 10: Recover Data after Dropping Table by mistake.
User D dropped one most important application table in ASM without any backup. Oracle introduced recyclebin feature in 10g. Please check whether the dropped table is in recyclebin by DBA_RECYCLEBINS view. If there is , try to recover data back by “flashback to before drop”. Or, we can use PRM-DUL for recovery.
Recovery steps by PRM-DUL
- OFFLINE the table space that the dropped table locates.
- Find the DATA_OBJECT_ID of dropped table by query data dictionary or logminer. If not successfully, then user has to recognize this table in No-dictionary mode.
- Start PRM-DUL, go to No-dictionary mode, and add all data files of dropped data file. Then SCAN DATABASE+SCAN TABLE from Extent MAP
- Locate the data table by DATA_OBJECT_ID in object tress, and insert data back by DataBridge
| SQL> select count(*) from “MACLEAN”.”TORDERDETAIL_HIS”;COUNT(*)———-984359
SQL> SQL> create table maclean.TORDERDETAIL_HIS1 as select * from maclean.TORDERDETAIL_HIS;
Table created.
SQL> drop table maclean.TORDERDETAIL_HIS;
Table dropped. |
We can find the general DATA_OBJECT_ID by logminer or similar method in “CASE 9”
| EXECUTE DBMS_LOGMNR.ADD_LOGFILE( LOGFILENAME => ‘/oracle/logs/log1.f’, OPTIONS => DBMS_LOGMNR.NEW);EXECUTE DBMS_LOGMNR.ADD_LOGFILE( LOGFILENAME => ‘/oracle/logs/log2.f’, OPTIONS => DBMS_LOGMNR.ADDFILE);Execute DBMS_LOGMNR.START_LOGMNR(DBMS_LOGMNR.DICT_FROM_ONLINE_CATALOG+DBMS_LOGMNR.COMMITTED_DATA_ONLY);
SELECT * FROM V$LOGMNR_CONTENTS ;
EXECUTE DBMS_LOGMNR.END_LOGMNR; |
Although, there is no DATA_OBJECT_ID, if the table amount is not big, we can manually recognize the data table
OFFLINE table space of dropped table
| SQL> select tablespace_name from dba_segments where segment_name=’TPAYMENT’;TABLESPACE_NAME——————————USERS
SQL> select file_name from dba_data_files where tablespace_name=’USERS’;
FILE_NAME —————————————————————- +DATA1/parnassus/datafile/users.263.843694795
SQL> alter tablespace users offline;
Tablespace altered. |
Start PRM-DUL in NON-DICT mode, and add all data to SCAN DATABASE+SCAN TABLE From Extents:
Add related ASM Disks and click ASM Analyze
Select the character set in Non-Dict mode
Select the data files of dropped table, and click scan
Generate database name and right click scan tables from extents:
Recognize TORDERDETAIL_HIS table which is mapped to DATA_OBJECT_ID=82641 manually and insert back to the database by DataBridge
FAQ
- How to get database character set?
You can find your database character by Oracle Alert.log
| [oracle@mlab2 trace]$ grep -i character alert_Parnassus.logDatabase Characterset is US7ASCIIDatabase Characterset is US7ASCIIalter database character set INTERNAL_CONVERT AL32UTF8Updating character set in controlfile to AL32UTF8
Synchronizing connection with database character set information Refreshing type attributes with new character set information Completed: alter database character set INTERNAL_CONVERT AL32UTF8 alter database national character set INTERNAL_CONVERT UTF8 Completed: alter database national character set INTERNAL_CONVERT UTF8 Database Characterset is AL32UTF8 Database Characterset is AL32UTF8 Database Characterset is AL32UTF8 |
- PRM-DUL failed with GC ” gc warning: Repeated allocation of very large block (appr.size 512000)”
So far, most of problem is caused by not recommended Java environment. Especially, on Linux, default java environment is redhat gcj java. ParnassusData suggest Open JDK 1.6 for PRM-DUL, and use $JAVA_HOME/bin/java –jar PRM-DUL.jar for PRM-DUL boot.
Open JDK For Linux download Link:
| Open jdk x86_64 for Linux 5 | http://pan.baidu.com/s/1qWO740O |
| Tzdata-java x86_64 for Linux 5 | http://pan.baidu.com/s/1gdeiF6r |
| Open jdk x86_64 for Linux 6 | http://pan.baidu.com/s/1mg0thXm |
| Open jdk x86_64 for Linux 6 | http://pan.baidu.com/s/1sjQ7vjf |
| Open jdk x86 for Linux 5 | http://pan.baidu.com/s/1kT1Hey7 |
| Tzdata-java x86 for Linux 5 | http://pan.baidu.com/s/1kT9iBAn |
| Open jdk x86 for Linux 6 | http://pan.baidu.com/s/1sjQ7vjf |
| Tzdata-java x86 for Linux 6 | http://pan.baidu.com/s/1kTE8u8n |
JDK on Other platform downloads:
| AIX JAVA SDK 7 | http://pan.baidu.com/s/1i3JvAlv |
| JDK Windows x86 | http://pan.baidu.com/s/1qW38LhM |
| JDK Windows x86-64 | http://pan.baidu.com/s/1qWDcoOk |
| Solaris JDK 7 x86-64bit | http://pan.baidu.com/s/1gdzgSvh |
| Solaris JDK 7 x86-32bit | http://pan.baidu.com/s/1mgjxFlQ |
| Solaris JDK 7 Sparc | http://pan.baidu.com/s/1pJjX3Ft |
Oracle JDK downloads:
- If you find PRM-DUL bug, how to report bug to ParnassusData?
ParnassusData recommend anyone to report bug, just send report_bugs@parnassusdata.com. Suggest submit bug environment, including Java environment and Oracle database Environment.
- What should I do if it PRM-DUL failed with
Error: no `server’ JVM at `D:\Program Files (x86)\Java\jre1.5.0_22\bin\server\jvm.dll’.
If user just installed JAVA Runtime Environment JRE, no JDK, please start PRM-DUL without –server option. This option does not exist in the version before JRE 1.5, and there is supposed to have an error.
ParnassusData suggests Open JDK 1.6 or above
Below link to download JDK 1.6
- Why does PRM-DUL display Chinese as messy code?
So far, there are two reasons for Chinese encoding problem:
- The OS does not have Chinese language pack, PRM-DUL can not display Chinese correctly
- If OS have language package installed, please use Open JDK1.6 or above. There might be some problem in JDK1.4
- Is there any forum for PRM-DUL?
Now we have Chinese forum for PRM-DUL, below is the link:
http://t.askmac.cn/forum-24-1.html
Find More
Resource: http://www.parnassusdata.com/resources/
Technical Support: service@parnassusdata.com
Sales: sales@parnassusdata.com
Download Software: http://www.parnassusdata.com/
Contact: http://www.parnassusdata.com/zh-hans/contact
Conclusion
ParnassusData Corporation, Shanghai, GaoPing Road No. 733 . China
Phone: (+86) 13764045638
ParnassusData.com
Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/parnassusData
Twitter: http://twitter.com/ParnassusData
Weibo: http://weibo.com/parnassusdata
Copyright©2013, ParnassusData and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is provided for information purposes only and the contents hereof are subject to change without notice. This document is not warranted to be error-free, nor subject to any other warranties or conditions, whether expressed orally or implied in law, including implied warranties and conditions of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose. We specifically disclaim any liability with respect to this document and no contractual obligations are formed either directly or indirectly by this document. This document may not be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, for any purpose, without our prior written permission.
Oracle and Java are registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners.
AMD, Opteron, the AMD logo, and the AMD Opteron logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Advanced Micro Devices. Intel and Intel Xeon are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation. All SPARC trademarks are used under license and are trademarks or registered trademarks of SPARC International, Inc. UNIX is a registered trademark licensed through X/Open Company, Ltd. 0410
Copyright © 2014 ParnassusData Corporation. All Rights Reserved.