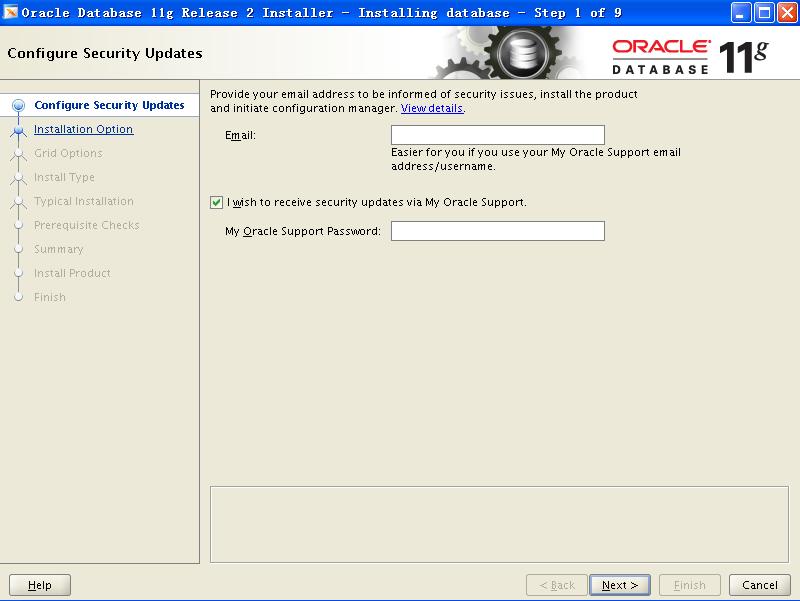
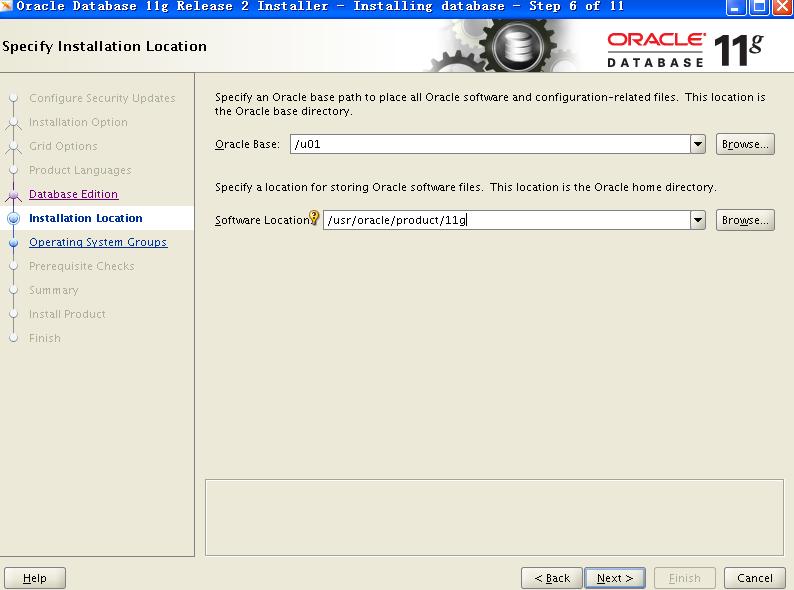
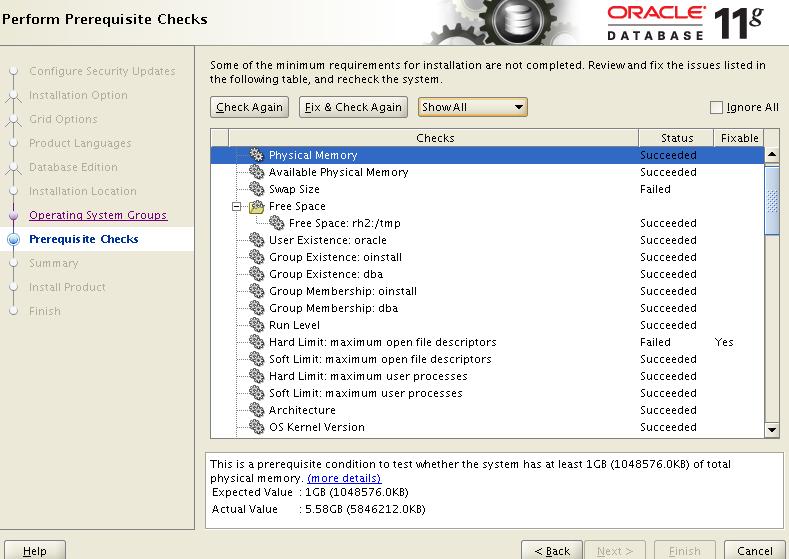
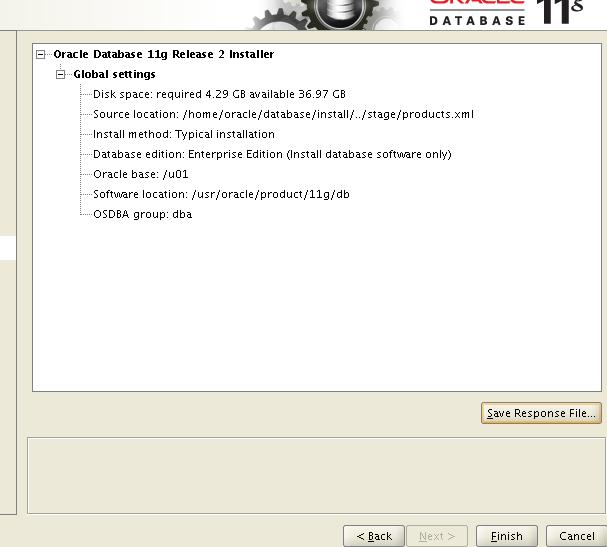
在对原SUN客户的公示中,Larry Ellison火药味十足地表示将在硬件领域与龙头老大IBM争霸。
公示向原SUN客户表示一下四点:
- 在Sparc架构上花费比SUN更多的开发费用。(当然光钱多,似乎有点形而上)
- 在Solaris操作系统上花费比SUN更多的开发费用。(Solaris已经十分健全,Oracle可能让其更自动化–auto tuning,更好的支持?大metalink计划?)
- 投入超过2倍于SUN的销售和技术专家服务于Sparc和Solaris的业务。(销售当然要多,这是Oracle的老路)
- 整合Oracle软件与Sun硬件,将明显提升原Sun的硬件性能。
公示结尾为larry Ellison的结语:
We’re in it to win it. IBM,we ‘re looking foward to competing with you in hardware business.
这份开战宣言表明了Oracle在硬件领域发展的决心,以及同IBM争霸的勇气。
两家同样以销售著名的公司(相对SUN等技术著名公司),将在未来几年内为我们展示新一轮的IT航母兼并战。