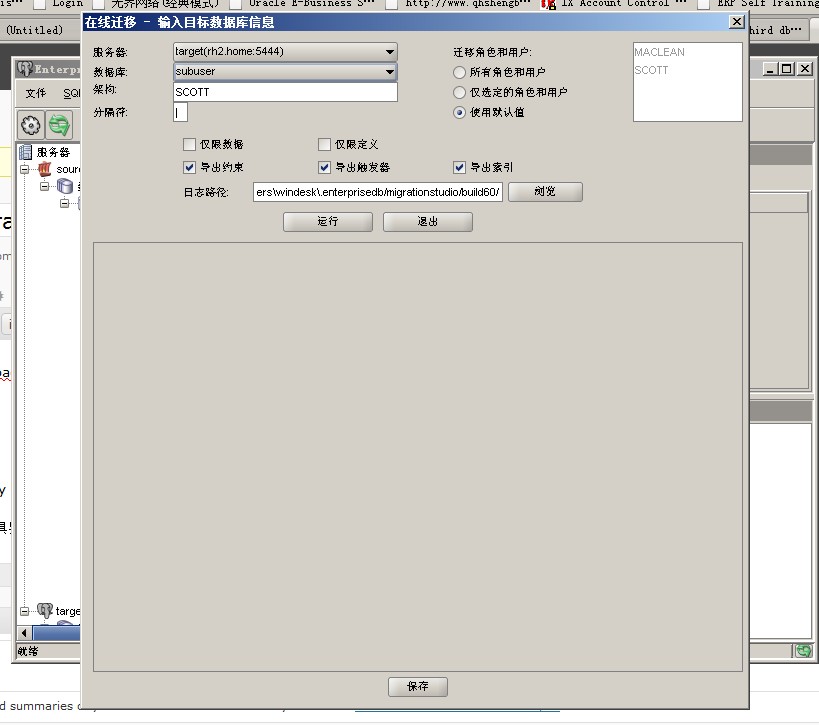
EntepriseDB 复制软件目前支持多种数据库到postgre的复制,其基本结构由发布者(Publication)与订阅者(Subscriptions)组成,Replication软件可针对来自不同类型数据库的多个发布者,将其数据复制到多个订阅者(Subscriptions)数据库中。
其可能的几种拓扑结构,如以下图:


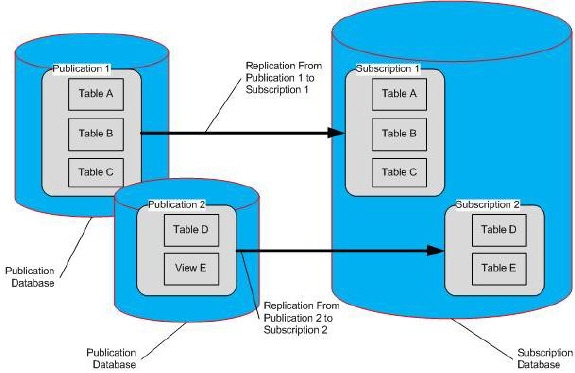
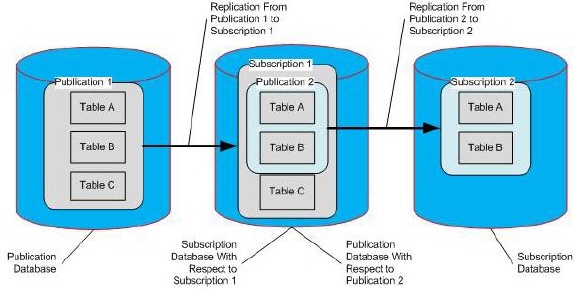
同Oracle中普通的物化视图一样,不支持对订阅者(Subscriptions)数据的修改–Changes must not be made to the data or the definitions of the subscription tables.
EnterpriseDB Replication软件的具体工作模式分成2种:即快照模式(snapshot)与同步模式(synchronization);在第一次启用同步前,需要进行一次快照操作,之后便可以进行较为轻量级同步操作了。若要使用同步模式(synchronization)则要求发布者所包含的表必须具有主键,而在仅使用快照模式的情景中则不需要。(Each table used in a publication must have a primary key with the exception of tables in snapshot-only publications, which do not require a primary key.) 以上模式均支持过滤器(fliter),即可以指定需要复制的具体数据子集。
EnterpriseDB Replication软件其同步(synchronization)模式复制的基本原理是基于trigger的,而非如Quest公司的shareplex或golden gate般抽取重做日志生成SQL的方式。trigger方式会在数据库源端产生一定的性能影响,若在mission critical的生产数据库中实施EDB replication 复制则需要考虑到这一点(这种情况下推荐使用Snapshot模式)。这可能是EDB复制软件比较不成熟的一点,就目前仅对Oracle日志文件的研究认识,挖掘重做日志进而实现数据复制的途径已经没有技术上的难点了。
以下发布者所包含的数据对象或表属性,将在订阅者成功建立时被复制到订阅者所在的数据库:
- Tables
- Views (for snapshot-only publications) – created as a table in the subscription database
- Primary keys
- Not null constraints
- Unique constraints
- Check constraints
- Indexes
注意:外键约束将不被复制
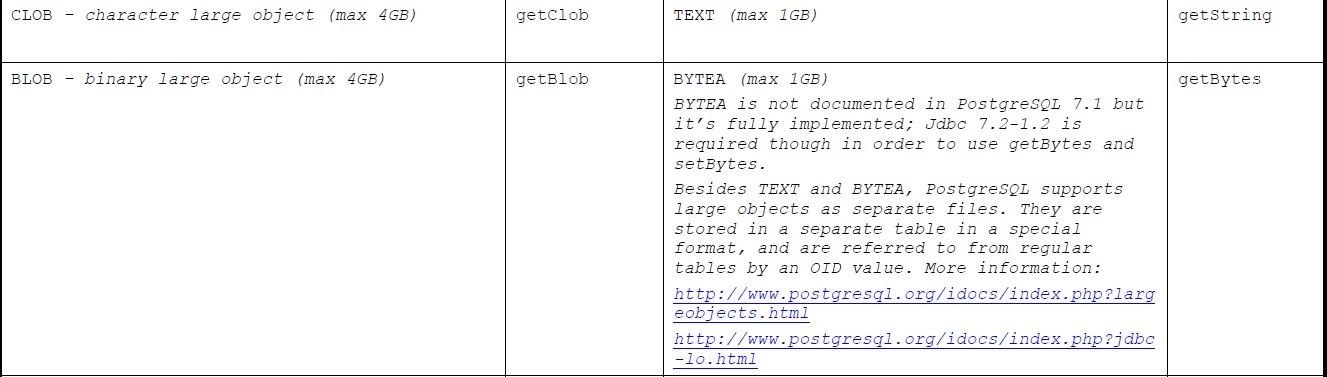
同时目前复制软件存在一定的限制,Oracle中的hash分区将不被复制,同时Oracle中包含以下数据类型列的表将无法复制:
- BFILE
- BINARY_DOUBLE
- BINARY_FLOAT
- MLSLABEL
- XMLTYPE
Oracle中包含以下数据类型列的表,将不能使用同步模式(synchronization replications):
- BLOB
- CLOB
- LONG
- LONG RAW
- NCLOB
- RAW
快照模式情况下,订阅者中复制目标表将首先被truncate截断,之后若订阅者数据库类型是Oracle则将使用JDBC驱动批量的将源端的数据INSERT进来,若数据库类型是EnterpriseDB advanced Sever则将使用Postgre中的Copy命令。
同步模式下复制软件通过在源端配置的触发器记录表,获知源端该时段内所经历的DML操作,进而在目标端生成对应修改的SQL语句(显然同源端的原始SQL不同)。
EnterpriseDB公司推荐在以下情景中使用快照模式以获得更好的性能:
- 表相对而言较小
- 在复制间隔中绝大多数数据行会被修改
而同步模式则更适宜于以下情景:
- 数据表非常巨大
- 在复制间隔中仅少数数据会被修改